by Susan Flantzer © Unofficial Royalty 2016

Anne, Princess Royal, Princess of Orange; Credit – Wikipedia
Anne, Princess Royal was the eldest daughter and the second child of King George II of Great Britain and Caroline of Ansbach. She was born a Princess of Hanover on November 2, 1709, at Schloss Herrenhausen in Hanover, now in the German state of Lower Saxony. At the time of her birth, her great-grandmother Sophia, Electress of Hanover was the heiress presumptive to Queen Anne of Great Britain in accordance with the Act of Settlement 1701, but Sophia died two months before Queen Anne died. Christened shortly after her birth at Schloss Herrenhausen, Anne was named after Queen Anne of Great Britain, her grandfather’s second cousin.
Anne had seven siblings:
- Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707 – 1751), married Princess Augusta of Saxe-Gotha, had issue, including King George III
- Princess Amelia (1711 – 1786), unmarried
- Princess Caroline (1713 – 1757), unmarried
- Prince George William (1717 – 1718), died in infancy
- Prince William, Duke of Cumberland (1721 – 1765), unmarried
- Princess Mary (1723 – 1772), married Friedrich II, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, had issue
- Princess Louise (1724 -1751), married Frederik V, King of Denmark and Norway

Anne, on the left, with two of her sisters, Amelia and Caroline; Credit – Wikipedia
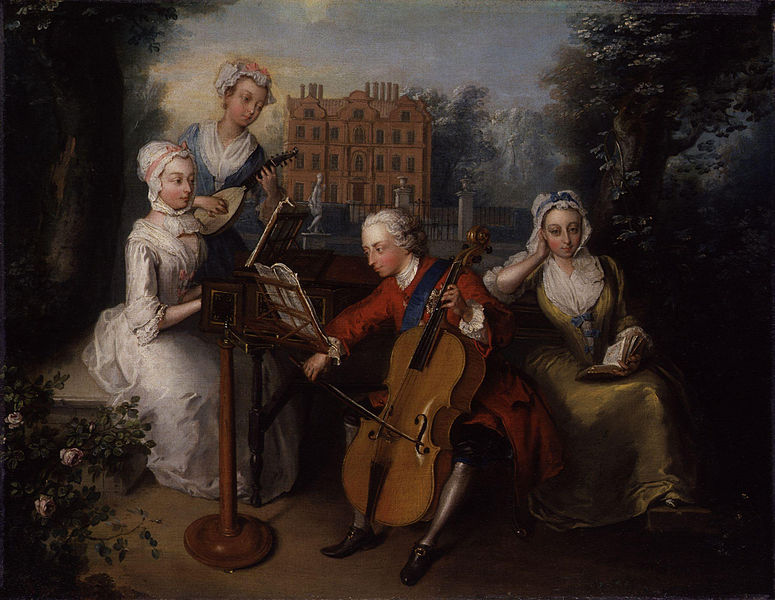
Anne playing the harpsichord, Caroline playing the lute, Frederick playing the cello, and Amelia reading; Credit – Wikipedia
When Anne was five years old in 1714, her grandfather succeeded Queen Anne as King George I of Great Britain, and she was then styled Her Royal Highness Princess Anne of Great Britain. Anne accompanied her parents and her two sisters, Amelia and Caroline, to England. Her elder brother, seven-year-old Frederick, now second in the line of succession to the British throne, was left in Hanover in the care of his great-uncle Ernst August, Prince-Bishop of Osnabrück. Frederick did not see his family again for 14 years. Certainly, this long separation during childhood was a factor in the negative relationship Frederick had with his parents as an adult.
Anne’s father, George, now Prince of Wales, had a very poor relationship with his father. The first big rift occurred because of a disagreement over the choice of godparents for the Prince and Princess of Wales’ short-lived son George William, born in 1717. The disagreement grew out of proportion, and George was placed under arrest. The result was that George and Caroline were exiled from St. James’ Palace. They moved into Leicester House in Leicester Square, London which became their chief residence for the rest of King George I’s reign. However, their children were kept at St. James’ Palace in the custody of their grandfather. Anne and her sister missed their parents tremendously. She lamented that her grandfather, the King, did not even visit them, saying, “He does not love us enough for that.” Little Prince George William died when he was three months old. His parents blamed King George I for his death which only worsened the relationship between father and son. In 1720, Anne became ill with smallpox, and for a few days, it was feared she might die. King George I knew that the death of a second grandchild while under his care would be on his conscience, and soon he reconciled with his son and daughter-in-law.
As the eldest daughter of the Prince and Princess of Wales, Anne felt a great deal of self-importance. She told her mother that she wished she had no brothers so that she could become Queen. When her mother disciplined her for the remark, Anne said, “I would die tomorrow to be Queen today.” Anne insisted that a lady-in-waiting stand beside her bed and read aloud until she fell asleep. Once, Anne took so long to fall asleep that the lady-in-waiting fell asleep in the middle of a chapter. The Princess of Wales decided to teach Anne a lesson. The next night she called Anne to her bedside and asked Anne to read aloud. When Anne tried to sit down, her mother told her to continue standing because she would be able to hear better. The Princess of Wales would not let Anne stop reading despite her complaining that she was tired and her throat was dry. Eventually, Anne began to cry and her mother decided that she had learned her lesson and scolded her for her treatment of the lady-in-waiting.
Anne was an excellent student. By the time she was five years old, she spoke, read, and wrote German and French, spoke English, and was learning history and geography. As she grew older, she became skilled at painting, embroidery, singing, dancing, and playing the harpsichord. The famous composer Georg Friedrich Handel was appointed her music master. Handel did not like teaching, but he made an exception for Anne, whom he called “Anne, flower of princesses.”
On June 11, 1727, Anne’s grandfather King George I, and Anne’s father succeeded him as King George II. On August 30, 1727, King George II created his eldest daughter Princess Royal, a title that had not been used since King Charles I first created it for his daughter Mary in 1642.

Anne, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange; Credit – Wikipedia
A proposed marriage with King Louis XV of France fell through because the French insisted that Anne convert to Roman Catholicism and Anne’s family refused. Bored with life at her father’s court, Anne did not want to be a spinster and was anxious to marry. Anne had been disfigured by smallpox and was not considered attractive. Among the few Protestant possibilities, was Willem IV, Prince of Orange. Willem had a spinal deformity, which affected his appearance, but Anne was so anxious to marry that said she would marry him even “if he were a baboon.” Anne and Willem were betrothed in 1733. On March 25, 1734, Anne and Willem married at the Chapel Royal in St. James’s Palace in London.
After enduring two miscarriages and two stillbirths, Anne and Willem had three children, but only two survived to adulthood. Through their son, they are ancestors of the Dutch Royal Family.
- Carolina of Orange-Nassau (1743 – 1787), married Karl Christian of Nassau-Weilburg, had issue
- Anna (born and died 1746)
- Willem V, Prince of Orange (1748 – 1806), married Princess Wilhelmina of Prussia, had issue

Willem IV, Prince of Orange; Anne, Princess of Orange and their two children Carolina and Willem; Credit – Wikipedia
When Anne and Willem arrived in the Netherlands, they took up residence at the Stadhouderlijk Hof in Leeuwarden, the provincial capital and seat of the States of Friesland (now in the Netherlands). Anne’s husband Willem was the posthumous son of Johan Willem Friso, Prince of Orange, who died from drowning at age 23, and his wife Maria Louise of Hesse-Kassel.
Upon his birth, Willem succeeded his father as Stadtholder of Friesland and as Stadtholder of Groningen. In 1722, he was elected Stadtholder of Guelders. In April 1747, the French army entered Flanders, threatening the Netherlands, which was weakened by internal division. The Dutch decided their country needed a single strong executive and turned to the House of Orange. Willem and his family moved from Leeuwarden to The Hague. On May 4, 1747, the States-General of the Netherlands named Willem General Stadtholder of all seven of the United Provinces of the Netherlands and made the position hereditary for the first time.

Willem IV, Prince of Orange; Credit – Wikipedia
Willem IV died at age 40 from a stroke on October 22, 1751, at Huis ten Bosch in The Hague and was buried in the crypt of the House of Orange in the Nieuwe Kerk (New Church) in Delft. He was succeeded by his three-year-old son Willem V with Anne serving as Regent.
As Regent, Anne was given all the powers normally given a hereditary Stadtholder of the Netherlands, except the military duties of the office, which were entrusted to Ludwig Ernst of Brunswick-Lüneburg. She was hard-working, but arrogant and imperious, which made her unpopular. The 1750s were years of increasing tension and commercial rivalry between the Netherlands and Great Britain, which placed her in a difficult position.

Anne, Princess of Orange; Credit – Wikipedia
Anne acted as Regent until her death from dropsy on January 12, 1759, at age 49 in The Hague, the Netherlands. As her son was underage, his paternal grandmother Marie Louise of Hesse-Kassel became Regent. When Marie Louise died in 1765, Anne’s daughter Carolina, served as Regent until Willem V turned 18 in 1766. Anne was buried with her husband in the crypt of the House of Orange in the Nieuwe Kerk (New Church) in Delft, the Netherlands.

The access to the royal crypt in the foreground; Credit – By Sander van der Wel from Netherlands – Royal grave tomb and the grave of Willem van Oranje, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=28146859
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
“Anne, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange.” Wikipedia. N.p.: Wikimedia Foundation, 30 Aug. 2016. Web. 10 Sept. 2016.
“John William Friso, Prince of Orange.” Wikipedia. N.p.: Wikimedia Foundation, 15 July 2016. Web. 10 Sept. 2016.
Susan. “King George II of Great Britain.” British Royals. Unofficial Royalty, 21 Dec. 2015. Web. 10 Sept. 2016.
Van Der Kiste, John. The Georgian Princesses. Phoenix Mill: Sutton Publishing, 2000. Print.
“William IV, Prince of Orange.” Wikipedia. N.p.: Wikimedia Foundation, 23 July 2016. Web. 10 Sept. 2016.
Williamson, David. Brewer’s British Royalty. London: Cassell, 1996. Print.
