by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2023
Principality of Lippe: Originally called Lippe-Detmold, the Principality of Lippe came into existence in 1789 when it was raised from a County within the Holy Roman Empire to a Principality. Leopold I, Count of Lippe-Detmold became the first Prince of Lippe.
At the end of World War I, Leopold IV, the last Prince of Lippe, was forced to abdicate on November 12, 1918. However, Leopold negotiated a treaty with the new government that allowed his family to remain in Lippe. Today the territory that encompassed the Principality of Lippe is located in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia.
*********************
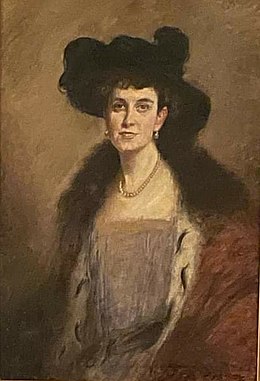
Portrait of Princess Anna by Bernhard Zickendraht, 1924, displayed in Detmold Castle; Credit – Wikipedia
Princess Anna of Ysenburg and Büdingen was the second of the two wives of Leopold IV, Prince of Lippe. Anna was born on February 10, 1886, in Büdingen, then in the Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine, now in the German state of Hesse. Originally, the House of Büdingen, a noble family, held control of Büdingen but in 1816, it was given to the Grand Duchy of Hessen-Darmstadt, later the Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine. Anna was the youngest of the eight children and the youngest of the seven daughters Bruno, 3rd Prince of Ysenburg and Büdingen and his second wife Countess Bertha of Castell-Rüdenhausen. Her paternal grandparents were Ernst Casimir II, 2nd Prince of Ysenburg and Büdingen and his wife Countess Thekla of Erbach-Fürstenau. Anna’s maternal grandparents were Adolf, Hereditary Count of Castell-Rüdenhausen and Baroness Marie of Thüngen.
Anna had seven older siblings:
- Princess Emma of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1870 – 1944), married Count Otto of Solms-Laubach, had four children
- Princess Marie of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1875 – 1952), unmarried
- Wolfgang, 4th Prince of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1877 – 1920), married Countess Adelheid of Rechteren-Limpurg, no children
- Princess Thekla of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1878 – 1950), married Manfred V, Prince of Collalto and San Salvatore, had four children
- Princess Mathilde of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1880 – 1947), married Cornelius, Baron Heyl of Herrnsheim, had five children
- Princess Helene of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1881 – 1951), unmarried
- Princess Hertha of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1883 – 1972), married Prince Albrecht of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, had one daughter Princess Ortrud of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg who married Ernst August IV, Hereditary Prince of Brunswick, Prince of Hanover – they are the parents of Prince Ernst August (V) of Hanover
Anna had two older half-sisters from her father’s first marriage to Princess Mathilde of Solms-Hohensolms-Lich:
- Princess Hedwig of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1863 – 1925), married (1) Botho, 1st Prince of Stolberg-Rossla, had four children (2) Count Kuno of Stolberg-Rossla, no children
- Princess Elisabeth of Ysenburg and Büdingen (1864 – 1946), married Rudolf, Baron of Thüngen, had four children

Büdingen Castle where Anna grew up; Credit – Von Sven Teschke – Eigenes Werk, CC BY-SA 2.0 de, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=31460
On November 21, 1911, at Büdingen Castle (link in German) in Büdingen, where Anna grew up, she married Count Ernst of Lippe-Weissenfeld, son of Count Franz of Lippe-Weissenfeld and Baroness Marie von Beschwitz. Less than three years later, Ernst was killed in action at Gołdap, then in the Kingdom of Prussia, now in Poland, on the Eastern Front during World War I, on September 11, 1914.
Anna and Ernst had one daughter:
- Princess Eleonore of Lippe-Weissenfeld (1913 – 1964), married Adolph Sweder Hubertus, Count of Rechteren-Limpurg, had two one son and one daughter
On April 26, 1922, in Büdingen, Germany, Anna became the second wife of Leopold IV, the last Prince of Lippe, the pretender to the throne of the Principality of Lippe. Following the German Empire’s defeat in World War I and the German Revolution of 1918-1919, Leopold IV was forced to renounce the throne on November 12, 1918, by the Lippe People’s and Soldiers’ Council. However, Leopold negotiated a treaty with the new government allowing his family to remain in Lippe.
Leopold and Anna had one son:
- Armin, Prince of Lippe (1924 – 2015) married Traute Becker, had one son
Leopold’s first wife Princess Bertha of Hesse-Philippsthal-Barchfeld died in 1919 and upon her marriage to Leopold in 1922, Anna became the stepmother of Leopold’s five children from his first marriage:
- Ernst, Hereditary Prince of Lippe (link in German) (1902 – 1987), married (1) Charlotte Ricken, divorced (2) Herta-Elise Weiland, had one son and one daughter
- Prince Leopold Bernhard of Lippe (1904 – 1965), unmarried
- Princess Karoline of Lippe (1905 – 2001), married Count Hans of Kanitz, had six daughters
- Prince Chlodwig of Lippe (1909 – 2000), married Veronika Holl, had one daughter
- Princess Sieglinde of Lippe (1915 – 2008), married Friedrich Carl Heldman, had two daughters and one son
During the rise of Nazism in Germany, all three of Leopold’s sons by his first wife Bertha became members of the Nazi Party. The eldest son the Hereditary Prince Ernst is reported to have been the first German prince to join the Nazi Party when he signed up in May 1928. Ernst’s brother Chlodwig joined the Nazi Party in 1931 and the other brother Leopold Bernhard joined in 1932. Hereditary Prince Ernst later became an SS-Major (Schutzstaffel Sturmbannführer) and held a high-ranking post in the SS Race and Settlement Main Office. The SS (Schutzstaffel) was the agency of security, surveillance, and terror in Nazi Germany and German-occupied Europe. The SS Race and Settlement Main Office was responsible for safeguarding the racial purity of the SS within Nazi Germany. At the end of World War II, Hereditary Prince Ernst of Lippe was taken prisoner by the Allies and took part in the Nuremberg Trials as a witness. The denazification tribunal in the Detmold administrative district classified Ernst as a Lesser Offender, Category III. He was not imprisoned but rather placed on probation for three years with a list of restrictions.
In addition to being pro-Nazi, both Hereditary Prince Ernst and Prince Khlodwig had made unequal marriages. Due to these circumstances, Leopold rewrote his will in 1947, indicating that Armin, his only child with his second wife, would succeed him as the head of the House of Lippe and become the administrator of the princely family’s properties such as the Residenzschloss Detmold (link in German), thereby disinheriting all three of his sons from his first marriage.

Christ Church in Detmold; Credit – Von Daniel Brockpähler – Eigene Fotografie, bearbeitet mit Photoshop von Nikater, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=8648403
Anna’s husband Leopold IV, the last Prince of Lippe died, aged 78, on December 30, 1949, in Detmold, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. He was buried with his first wife Bertha at the Christ Church in Detmold (link in German). Leopold’s second wife Anna survived him by thirty-one years, dying on February 8, 1980, in Detmold at the age of 94, and was also buried at Christ Church.
Anna and Leopold’s son Armin was head of the House of Lippe from 1949 until he died in 2015. Armin’s only child Stephan, Prince of Lippe (born 1959) succeeded him as head of the House of Lippe. Stephan married Countess Maria of Solms-Laubach and they had three sons and two daughters.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Bruno, Prince of Ysenburg and Büdingen (2022) Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bruno,_Prince_of_Ysenburg_and_B%C3%BCdingen (Accessed: 19 July 2023).
- De.wikipedia.org. 2020. Leopold IV. (Lippe). [online] Available at: <https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leopold_IV._(Lippe)> [Accessed 13 October 2020].
- En.wikipedia.org. 2020. Leopold IV, Prince Of Lippe. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leopold_IV,_Prince_of_Lippe> [Accessed 13 October 2020].
- Flantzer, S. (2023) Leopold IV, Prince of Lippe, Unofficial Royalty. Available at: https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/leopold-iv-prince-of-lippe/ (Accessed: 19 July 2023).
- Mehl, Scott, 2018. Lippe Royal Burial Sites. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/former-monarchies/german-royals/principality-of-lippe/lippe-royal-burial-sites/> [Accessed 13 October 2020].
- Petropoulos, Jonathan, 2009. Royals And The Reich. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Princess Anna of Ysenburg and Büdingen (2022a) geni_family_tree. Available at: https://www.geni.com/people/Princess-Anna-of-Ysenburg-and-B%C3%BCdingen/6000000009136870908 (Accessed: 19 July 2023).
- Princess Anna of Ysenburg and Büdingen (2022) Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Princess_Anna_of_Ysenburg_and_B%C3%BCdingen (Accessed: 19 July 2023).


























