by Susan Flantzer © Unofficial Royalty 2019
Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld/Saxe-Coburg and Gotha: In 1675, Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg died. Initially, his seven sons collectively governed the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, as set out in their father’s will. In 1680, the seven brothers concluded a treaty of separation, with each brother getting a portion of the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha Altenburg and becoming a Duke. One of the seven new duchies was the Duchy of Saxe-Saalfeld and Johann Ernst, one of the seven sons of Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg became the first Duke of Saxe-Saalfeld. When two of his brothers died without male heirs, Johann Ernst took possession of Coburg (in 1699) and Römhild (in 1714). In 1699, Johann Ernst’s title changed to Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld.
In 1825, 145 years after the initial split, another line became extinct and there was another split between three surviving duchies. Ernst III, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld became Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. For more information on the switch, see Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld/Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Index.
On November 9, 1918, after the German Empire lost World War I, the Workers’ and Soldiers Council of Gotha, deposed the last Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Charles Edward, a grandson of Queen Victoria. Five days later, he signed a declaration relinquishing his rights to the throne. The territory that encompassed the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha is now in the German states of Bavaria and Thuringia.
********************

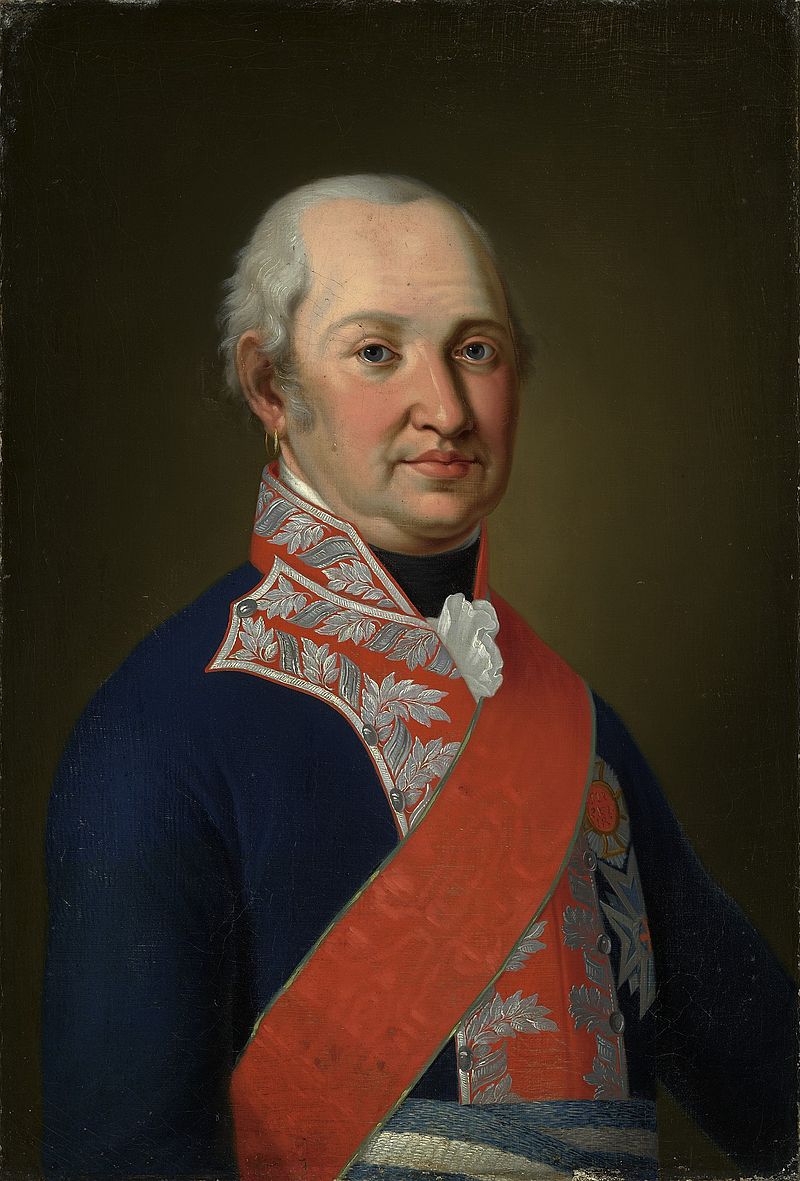
Johann Ernst IV, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld; Credit – Wikipedia
The founder of the House of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, the precursor to the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, and the ancestor of all British monarchs since Queen Victoria, Johann Ernst IV, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld was born on August 22, 1658, in Gotha, Duchy of Saxe-Gotha, now in Thuringia, Germany. He was the fifteenth of the eighteen children and the eleventh of the twelve sons of Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha and Elisabeth Sophie of Saxe-Altenburg.
Johan Ernst had seventeen siblings. The birth of his siblings spanned 25 years. Three siblings of his siblings died in December 1657 from smallpox and six died in infancy.
- Johann Ernst (born and died 1638), died in infancy
- Elisabeth Dorothea (1640 – 1709), married Ludwig VI, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt, had six sons and two daughters
- Johann Ernst (1641 – 1657), died as a teenager from smallpox
- Christian (born and died 1642), died in infancy
- Sophie (1643 – 1657), died as a teenager from smallpox
- Johanna (1645 – 1657), died in childhood from smallpox
- Friedrich I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg (1646 – 1691), married (1) Magdalena Sibylle of Saxe-Weissenfels, had two sons and six daughters (2) Christine of Baden-Durlach no children
- Albrecht, Duke of Saxe-Coburg (1648 – 1699), married (1) Marie Elisabeth of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, had one son who died in infancy (2) Susanne Elisabeth Kempinsky, no children
- Bernhard I, Duke of Saxe-Meiningen (1649 – 1706), married (1) Marie Hedwig of Hesse-Darmstadt, had six sons and one daughter (2) Elisabeth Eleonore of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, had two sons and three daughters
- Heinrich, Duke of Saxe-Römhild (1650 – 1710), married Marie Elisabeth of Hesse-Darmstadt, no children
- Christian, Duke of Saxe-Eisenberg (1653 – 1707). married (1) Christiane of Saxe-Merseburg, had one daughter (2) Sophie Marie of Hesse-Darmstadt, no children
- Dorothea Maria (1654 – 1682), unmarried
- Ernest, Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen (1655 – 1715), married Sophie of Waldeck, had three sons and two daughters
- Johann Philip (born and died 1657), died in infancy
- Johanna Elisabeth (born and died in 1660)
- Johann Philip (1661 – 1662), died in infancy
- Sophie Elisabeth (born and died in 1663), died in infancy
Johann Ernst was the youngest of his father’s seven surviving sons. All seven surviving sons were raised and educated as future rulers because Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha disliked primogeniture in which the eldest son is the sole heir. In 1672, the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha and the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg were united under Ernst I when Friedrich Wilhelm III, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg, the cousin of Ernst’s wife Elisabeth of Saxe-Altenburg, died childless. Ernst I was now the Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg.

Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, father of Johann Ernst; Credit – Wikipedia
On March 26, 1675, Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg died. Initially, all seven brothers governed the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg, as set out in their father’s will. On February 24, 1680, the seven brothers concluded a treaty of separation, with each brother getting a portion of the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha Altenburg and becoming a Duke.
- Friedrich I became Duke of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
- Albrecht became Duke of Saxe-Coburg
- Bernhard I became Duke of Saxe-Meiningen
- Heinrich became Duke of Saxe-Römhild
- Christian became Duke of Saxe-Eisenberg
- Ernst became Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen
- Johann Ernst IV became Duke of Saxe-Saalfeld
The map below shows the combined territory of Saxe-Gotha and Saxe-Altenburg from 1672 before it was again divided in 1680.
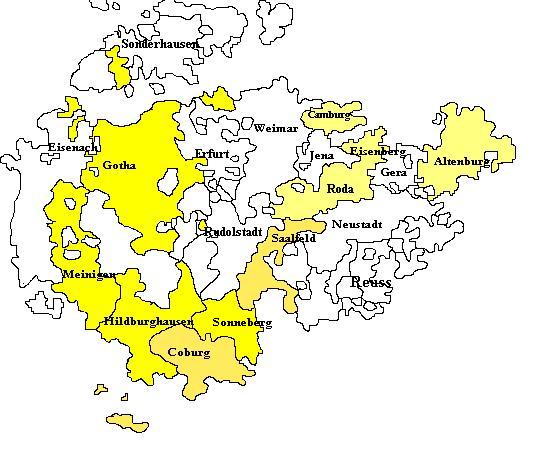
Credit – Wikipedia
Joann Ernst’s elder brothers Albrecht of Saxe-Coburg and Heinrich of Saxe-Römhild died without male heirs. Upon their deaths, Johann Ernest took possession of Coburg (in 1699) and Römhild (in 1714). In 1699, Johann Ernst became Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld.
In 1825, 145 years after the initial split, the House of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg became extinct and the Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg was split. Saxe-Gotha passed to the Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, who gave Saalfeld to the Duke of Saxe-Meiningen. The Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen received Saxe-Altenburg and gave the district of Hildburghausen to Saxe-Meiningen.
As a result:
- Ernst III, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld became Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. Ernst I had two sons: his heir, the future Ernst II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, the husband of Queen Victoria.
- The Duchy of Saxe-Hildburghausen ceased to exist. Friedrich, Duke of Saxe-Hildburghausen became Friedrich, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg.
- Bernhard II, Duke of Saxe-Meinigen remained Duke of Saxe-Meiningen but had the additional land that encompassed Hildburghausen and Saalfeld.
- The Duchies of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Saxe-Altenburg, and Saxe-Meiningen remained the same until the abolition of the German monarchies after World War I.
On February 18, 1680, Johann Ernst married Sophie Hedwig of Saxe-Merseburg, daughter of Christian I, Duke of Saxe-Merseburg and Christiana of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg. Three years earlier, Sophie Hedwig’s sister Christiane married Christian, Duke of Saxe-Eisenberg, Johann Ernst’s brother. Sophie Hedwig, aged 25, died in childbirth on August 2, 1686, after giving birth to a stillborn son. She was buried in the Johanneskirche in Saalfeld, Duchy of Saxe-Saalfeld, now in Thuringia, Germany.
Johann Ernst and Sophie Hedwig had three children:
- Christiane Sophie (1681 – 1697), died as a teenager
- Christian Ernst II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld (1683 – 1745), morganatically married Christiane Fredericka of Koss, no children
- Charlotte Wilhelmine (1685 – 1767), married Philip Reinhard, Count of Hanau-Münzenberg, no children

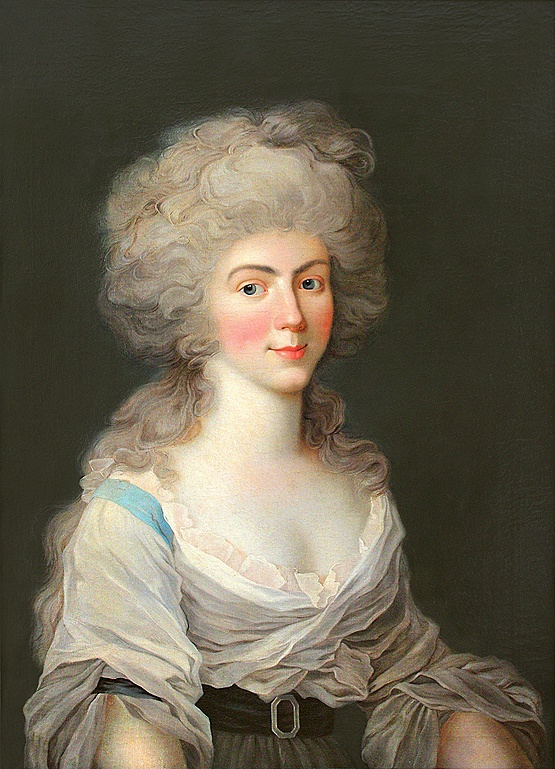
Charlotte Johanna of Waldeck-Wildungen, Johann Ernst’s second wife; Credit – Wikipedia
Four years after his first wife’s death, Johann Ernst married Charlotte Johanna of Waldeck-Wildungen on December 2, 1690. Charlotte Johanna was the daughter of Count Josias II of Waldeck-Wildungen and Countess Wilhelmine Christine of Nassau-Siegen. Charlotte Johanna died on February 1, 1699, at the age of 34 and was buried in the Johanneskirche in Saalfeld, Duchy of Saxe-Saalfeld, now in Thuringia, Germany. Johann Ernst did not marry again.
Johann Ernst and Charlotte Johanna had eight children:
- Wilhelm Friedrich (1691 – 1720), unmarried
- Karl Ernst (1692 – 1720), unmarried
- Sophia Wilhelmina (1693 – 1727), married Friedrich Anton, Prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, had one son and two daughters
- Henriette Albertine (1694 – 1695), died in infancy
Luise Amalia (1695 – 1713), died as a teenager - Charlotte (born and 1696), died in infancy
- Franz Josias, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld (1697 – 1764), married Anna Sophie of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, had four sons and four daughters
- Henriette Albertine (1698 – 1728), unmarried

Schloss Saalfeld; Credit – Wikipedia
In 1677, Ernst’s elder brothers Albrecht and Bernhard started the construction of a castle on the site of a former Benedictine monastery in Saalfeld. When Johann Ernst became Duke of Saxe-Saalfeld in 1680, he took over the construction of the unfinished castle. He moved into the castle, Schloss Saalfeld, in 1691 and it was his residence for the remainder of his life. Today the castle serves as the administrative seat of the district Saalfeld-Rudolstadt and the castle gardens are a public park.

Johanneskirche, the burial site of Johann Ernst and his two wives; Von Michael Sander – Eigenes Werk, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=3775005
Johann Ernst IV, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld died at Schloss Saalfeld on February 17, 1729, at the age of 70. He was buried with his two wives in the crypt at the Johanneskirche (link in German) in Saalfeld, Duchy of Saxe-Saalfeld, now in Thuringia, Germany.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld/Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Resources at Unofficial Royalty
- Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld/Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Index
- Profiles: Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Rulers and Consorts
- Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Royal Dates
- Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld/Saxe-Coburg and Gotha Royal Burial Sites
Works Cited
- De.wikipedia.org. (2019). Johann Ernst (Sachsen-Coburg-Saalfeld). [online] Available at: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Johann_Ernst_(Sachsen-Coburg-Saalfeld) [Accessed 5 Feb. 2019].
- De.wikipedia.org. (2019). Schloss Saalfeld. [online] Available at: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schloss_Saalfeld [Accessed 5 Feb. 2019].
- En.wikipedia.org. (2019). John Ernest IV, Duke of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Ernest_IV,_Duke_of_Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld [Accessed 5 Feb. 2019].
- En.wikipedia.org. (2019). Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld [Accessed 5 Feb. 2019].
- En.wikipedia.org. (2019). Saxe-Gotha. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saxe-Gotha [Accessed 5 Feb. 2019].


































