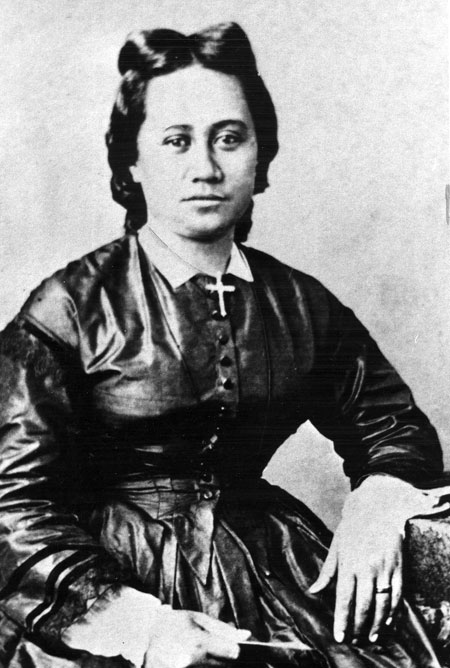by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2024
The Hawaiian Islands, located in the Pacific Ocean, were originally divided into several independent chiefdoms. The Kingdom of Hawaii was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great of the independent island of Hawaii, conquered the independent islands of Oahu, Maui, Molokai, and Lanai, and unified them under one government and ruled as Kamehameha I, King of the Hawaiian Islands. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauai and Niihau voluntarily joined the Kingdom of Hawaii. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.
In 1778, British explorer James Cook visited the islands. This led to increased trade and the introduction of new technologies and ideas. In the mid-19th century, American influence in Hawaii dramatically increased when American merchants, missionaries, and settlers arrived on the islands. Protestant missionaries converted most of the native people to Christianity. Merchants set up sugar plantations and the United States Navy established a base at Pearl Harbor. The newcomers brought diseases that were new to the indigenous people including influenza, measles, smallpox, syphilis, tuberculosis, and whooping cough. At the time of James Cook’s arrival in 1778, the indigenous Hawaiian population is estimated to have been between 250,000 and 800,000. By 1890, the indigenous Hawaiian population declined to less than 40,000.
In 1893, a group of local businessmen and politicians composed of six non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects, five American nationals, one British national, and one German national overthrew Queen Liliuokalani, her cabinet, and her marshal, and took over the government of the Kingdom of Hawaii. This led to the 1898 annexation of Hawaii as a United States territory. On August 21, 1959, Hawaii became the 50th state of the United States.
In 1993, one hundred years after the Hawaiian monarchy was overthrown, the United States Congress passed and President Bill Clinton signed the Apology Resolution which “acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and further acknowledges that the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the Kingdom of Hawaii or through a plebiscite or referendum”. As a result, the Hawaiian sovereignty movement, a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom in Hawaii, was established along with ongoing efforts to redress the indigenous Hawaiian population.
********************

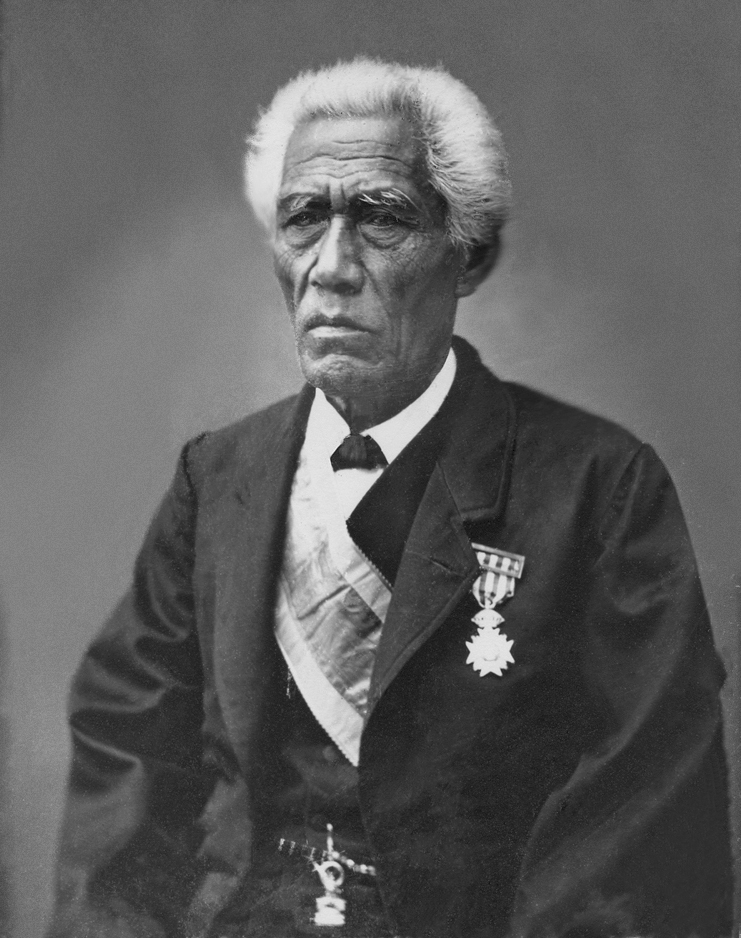
John Owen Dominis, Prince Consort of the Hawaiian Islands; Credit – Wikipedia
The husband of Queen Liliuokalani, the only Queen Regnant and the last monarch of the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands, John Owen Dominis was born on March 10, 1832, in Schenectady, New York. He was the youngest of the three children and the only son of John Dominis (1796 – 1846), originally from Trieste, then part of the Austrian Empire, now in Italy, and American-born Mary Lambert Jones. John had two older sisters Mary Elizabeth Dominis (1825 – 1838), Frances Ann Dominis (1829 – 1842), who both died when they were thirteen years old.

John’s father Captain John Dominis; Credit – Wikipedia
Being a sea captain, John’s father was frequently absent from home. He was involved in the Old China Trade and the fur trade in the Pacific Northwest with the British Hudson’s Bay Company. Captain John frequently stopped in the Hawaiian Islands to conduct business and resupply. Captain John, his wife Mary, and their son John relocated to Honolulu, on the island of Oahu, Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands in 1837. They left their two daughters in the United States to complete their education but they both died at the age of thirteen.

Washinton Place in Honolulu; Credit – By Frank Schulenburg – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=146081316
King Kamehameha III awarded some land to the family in 1842 as a settlement of a lawsuit with the British Consul Richard Charlton. Captain John continued to take voyages to raise money for the construction of a house. In 1846, Captain John sailed for China to purchase Chinese-made furniture for the nearly complete house. The ship was lost at sea, and John’s mother Mary became a widow. To make ends meet, Mary rented out rooms to boarders. One of the first boarders was Anthony Ten Eyck, an American Commissioner to the Hawaiian Islands who established the American Legation in the house. Ten Eyck named the house Washington Place on February 22, 1848 after George Washington in celebration of the first president’s birthday. The Dominis family continued to live at Washington Place. It eventually became the private residence of John and his wife Queen Liliuokalani, and they both died at Washington Place. Later Washington Place became the official residence of the Governor of Hawaii, and in 2007, it was designated as a National Historic Landmark. The current governor’s residence, built in 2008, is located on the same grounds as Washington Place.
John attended a school next to the Royal School, founded for the children of the native Hawaiian nobility, and he would climb the fence to observe the princes and princesses, and became friends with them. It was there that he first met his future wife, then Princess Liliuokalani. When John finished his schooling, he worked as a mercantile clerk in San Francisco, and as a clerk in a Honolulu commercial house. By 1856, he was a staff member to Prince Lot Kapuāiwa, the future King Kamehameha V, and then a secretary to King Kamehameha IV. John and Liliuokalani became romantically involved.

The future Queen Liliuokalani: Credit – Wikipedia
On September 16, 1862, John and Liliuokalani were married in an Anglican ceremony by Reverend Samuel Chenery Damon, a missionary to Hawaii and pastor of the Seamen’s Bethel Church in Honolulu. The couple moved into the Dominis residence, Washington Place in Honolulu. However, the marriage was not happy and was childless. John chose to socialize without Liliuokalani and his mother Mary looked down upon her non-caucasian daughter-in-law. Liliuokalani noted in her memoir that her mother-in-law considered her an “intruder” but became more affectionate in her later years.
John’s marriage to Liliuokalani and his close friendship with King Kamehameha V brought him many honors including:
- Knight Commander of the Royal Order of Kamehameha I and the Royal Order of Kalākaua
- Member of the Privy Council of the Hawaiian Kingdom (1863 – 1886)
- Member of the House of Nobles (1864 – 1886)
- Royal Governor of Oahu (1864 – 1886)
- Royal Governor of Maui (1878 – 1886)
- Lieutenant General and Commander in Chief (appointed 1886)
- Served on the Board of Health, Board of Education, Bureau of Immigration, and was Quartermaster General and Commissioner of Crown Lands

John’s illegitimate son John ʻAimoku Dominis with Liliuokalani in 1913; Credit – Wikipedia
John had an illegitimate son John ʻAimoku Dominis (1883 – 1917) with Mary Purdy Lamiki ʻAimoku, his wife’s servant. Liliʻuokalani accepted her husband’s unfaithfulness and adopted her husband’s son in 1910. John ʻAimoku Dominis married Sybil Frances Kahulumanu McInerny in 1911, and the couple had three children. He died on July 7, 1917, aged thirty-four, after suffering from a long illness.
Upon the death of her brother King Kalākaua on January 20, 1891, Lilluokalani became the first and the only female monarch of the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands, and John became Prince Consort. John Owen Dominis, aged fifty-nine, died less than a year later on August 27, 1891, at their Washington Place home, and was buried in the Mauna Ala Royal Mausoleum in Honolulu. Due to overcrowding, in 1907, the Territory of Hawaii allocated $20,000 for the construction of a separate underground vault for the Kalākaua family. John’s coffin and the coffins of the Kalākaua family were transferred to the new underground Kalākaua Crypt in a ceremony on June 24, 1910, officiated by his wife, the former Queen Liliuokalani.

Burial crypts of John Dominis (left) & Queen Liliuokalani (middle) in the Kalākaua Crypt; Credit – www.findagrave.com
Two years after John’s death, in 1893, a group of local businessmen and politicians composed of six non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects, five American nationals, one British national, and one German national overthrew Queen Liliuokalani and took over the government of the Kingdom of Hawaii. This led to the 1898 annexation of Hawaii as a United States territory. On August 21, 1959, Hawaii became the 50th state of the United States. Liliʻuokalani survived her husband by twenty-six years, dying on November 11, 1917, at the age of seventy-nine at her home, Washington Place in Honolulu, Hawaii. She was interred in Kalākaua Crypt next to John’s burial crypt on the grounds of the Royal Mausoleum of Mauna ʻAla in Honolulu, Hawaii.
Works Cited
- Flantzer, Susan. (2024). Lilluokalani, Queen of the Hawiian Islands. Unofficial Royalty. https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/liliuokalani-queen-of-the-hawaiian-islands/
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024). John Owen Dominis. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Owen_Dominis
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Hawaiian Kingdom. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hawaiian_Kingdom
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024). Mary Dominis. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mary_Dominis
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Royal Mausoleum (Mauna ʻAla). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Mausoleum_(Mauna_%CA%BBAla)
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024). Washington Place. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Washington_Place