by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2024
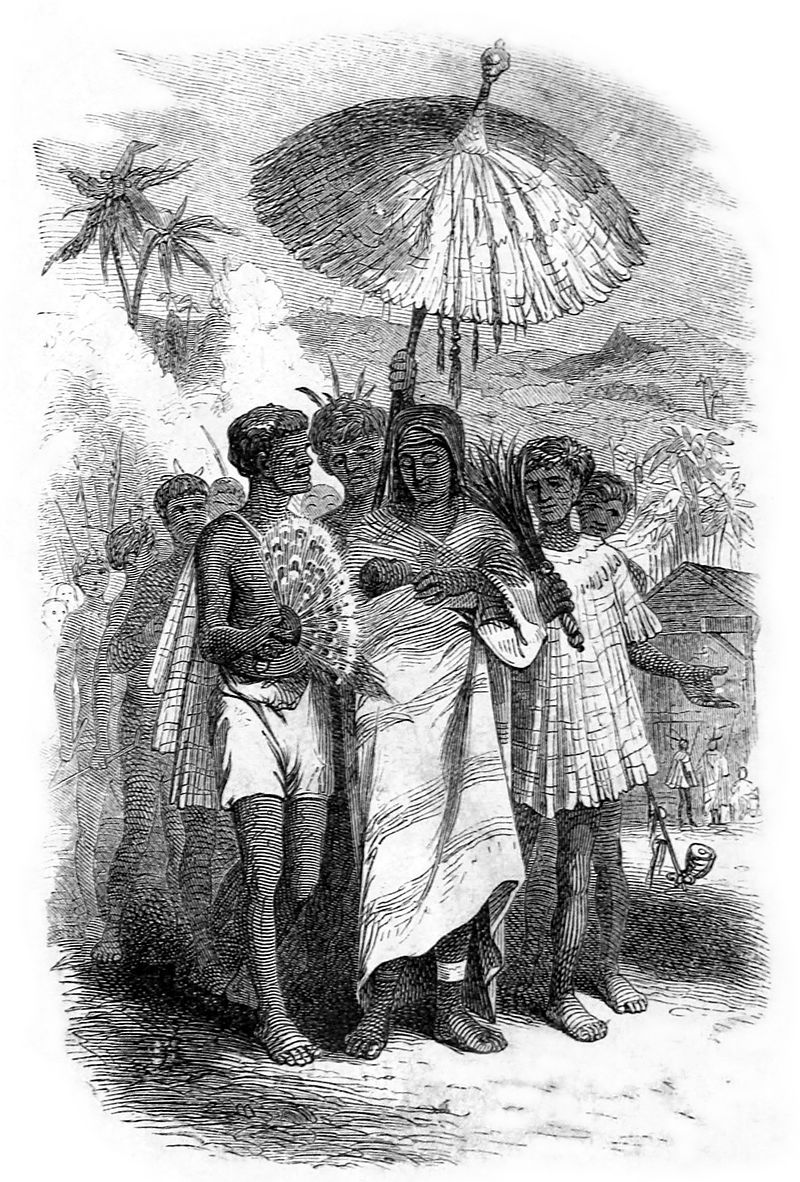
The Hawaiian Islands, located in the Pacific Ocean, were originally divided into several independent chiefdoms. The Kingdom of Hawaii was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great of the independent island of Hawaii, conquered the independent islands of Oahu, Maui, Molokai, and Lanai, and unified them under one government and ruled as Kamehameha I, King of the Hawaiian Islands. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauai and Niihau voluntarily joined the Kingdom of Hawaii. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.
In 1778, British explorer James Cook visited the islands. This led to increased trade and the introduction of new technologies and ideas. In the mid-19th century, American influence in Hawaii dramatically increased when American merchants, missionaries, and settlers arrived on the islands. Protestant missionaries converted most of the native people to Christianity. Merchants set up sugar plantations and the United States Navy established a base at Pearl Harbor. The newcomers brought diseases that were new to the indigenous people including influenza, measles, smallpox, syphilis, tuberculosis, and whooping cough. At the time of James Cook’s arrival in 1778, the indigenous Hawaiian population is estimated to have been between 250,000 and 800,000. By 1890, the indigenous Hawaiian population declined had to less than 40,000.
In 1893, a group of local businessmen and politicians composed of six non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects, five American nationals, one British national, and one German national overthrew Queen Liliʻuokalani, her cabinet, and her marshal, and took over the government of the Kingdom of Hawaii. This led to the 1898 annexation of Hawaii as a United States territory. On August 21, 1959, Hawaii became the 50th state of the United States.
In 1993, one hundred years after the Hawaiian monarchy was overthrown, the United States Congress passed and President Bill Clinton signed the Apology Resolution which “acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and further acknowledges that the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the Kingdom of Hawaii or through a plebiscite or referendum”. As a result, the Hawaiian sovereignty movement, a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom in Hawaii, was established along with ongoing efforts to redress the indigenous Hawaiian population.
********************
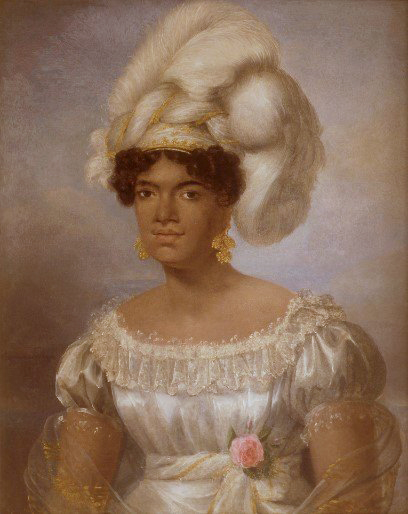
Kamāmalu, Queen Consort of the Hawaiian Islands; Credit – Wikipedia
Kamāmalu was the favorite of the five wives of Kamehameha II, King of the Hawaiian Islands, and was Queen Consort from 1819 – 1824, until her death and the death of her husband from measles. Born circa 1802 in Kawaihae, Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands, she was the eldest daughter of Kamehameha I, King of the Hawaiian Islands and one of his wives, Queen Kalākua Kaheiheimālie. King Kamehameha I had many wives and many children. The exact number is debated because documents that recorded the names of his wives were destroyed. While he had many wives and children, only his children from his highest-ranking wife Queen Keōpūolani succeeded him to the throne.
Kamāmalu had one half-sister from her mother’s first marriage to Prince Kalaʻimamahu, Chief Priest of ʻIo and Kāne, and a half-brother of King Kamehameha I:
Kekāuluohi (1794 – 1845), married (1) King Kamehameha I, no children (2) King Kamehameha II, no children (3) Charles Kanaʻina, had two sons, only one survived childhood, William Charles Lunalilo who reigned as King Lunalilo of the Hawaiian Islands from his election on January 8, 1873, until his death a year later
Kamāmalu had three full siblings from her mother’s second marriage to King Kamehameha I:
- Prince Liholiho-i-Kaiwi-o-Kamehameha (born 1795), died in infancy
- Prince Kamehameha Kapauaiwa (born circa 1801), died in infancy
- Princess Kīnaʻu (born circa 1805 – 1839), also known as Elizabeth Kīnaʻu, married (1) her half-brother King Kamehameha II, no children (2) Kahalaiʻa Luanuʻu, a grandson of King Kamehameha I, no children (3) Mataio Kekūanaōʻa, governor of the island of Oʻahu, had four sons and one daughter including King Kamehameha IV and King Kamehameha V

Kamehameha II, King of the Hawaiian Islands; Credit – Wikipedia
Kamāmalu was one of the five wives of King Kamehameha II, the last Hawaiian king to practice polygamy. She was betrothed to her half-brother Kamehameha II from birth and they were married when she was twelve and he was about seventeen. Kamehameha II had no children with any of his five wives:
- Kamāmalu (circa 1802 – 1824), Kamehameha II’s favorite wife, his half-sister
- Kīnaʻu (circa 1805 – 1839), Kamehameha II’s half-sister
- Kekāuluohi (1794 – 1845), Kamehameha II’s cousin
- Pauahi (circa 1804–1826), often referred to as often referred to as Kalanipauahi, Kamehameha II’s niece
- Kekauʻōnohi (circa 1805 – 1851), Kamehameha II’s niece
On May 14, 1819, Kamehameha I, King of the Hawaiian Islands died and his 22-year-old son Kamehameha II became King of the Hawaiian Islands and Kamāmalu became Queen Consort.
On April 16, 1822, English missionary William Ellis arrived in the Hawaiian Islands with a gift from King George IV of Great Britain, the Prince Regent, a schooner with six guns, to add to the Kingdom of Hawaiian Island’s fleet of ships. Kamehameha II wanted to travel to Great Britain to thank King George IV and to encourage closer diplomatic ties between their two kingdoms. All Kamehameha II’s advisors, including his mother Keōpūolani and his co-regent Kaʻahumanu, were opposed to the trip. After the death of his mother on September 16, 1823, Kamehameha II was determined to travel to Great Britain.

King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu in the Royal Box at the Theatre Royal in Drury Lane; Credit – Wikipedia
King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu arrived in Great Britain on May 17, 1824. Kamāmalu attracted much attention for her clothing – many society women asked their hatmakers to make turbans like the ones Kamāmalu wore – and because she was strikingly beautiful and six and a half feet tall. Kamehameha II and Kamāmalu toured London, visiting Westminster Abbey but Kamehameha II refused to enter because he did not want to desecrate the British royal burial place “with his presence or his feet stepping in that area.” The royal couple attended the opera and ballet at the Royal Opera House in Covent Garden, London, and a play at the Theatre Royal in Drury Lane, London.
King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu were scheduled to meet King George IV on June 21, 1824, but the meeting had to be canceled because Kamāmalu became ill. Members of the Hawaiian entourage had caught measles and they had no natural immunity because the people of the Hawaiian Islands had lived in isolation until their contact with Europeans. The Hawaiian entourage was likely exposed to measles on their June 5 visit to the Royal Military Asylum, an orphanage for the children of military parents that was known for its epidemics of childhood diseases. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, epidemics of measles, smallpox, and other diseases threatened to wipe out the entire Native Hawaiian population and disrupted the culture and lives of the islands’ residents.
Twenty-one-year-old Queen Kamāmalu died on July 8, 1824. Her grief-stricken husband King Kamehameha II died six days later on July 14, 1824, at the age of twenty-six. King Kamehameha II lay in state at the Caledonian Hotel in London on July 17, 1824, and large crowds paid their respects. On the following day, the coffins of King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu were placed in the crypt of St Martin-in-the-Fields Church in London, awaiting the voyage back to the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands.

HMS Blonde, the British ship that transported the coffins of King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu back to Hawaii; Credit – Wikipedia
In August 1824, the coffins of King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu left Great Britain on the Royal Navy frigate HMS Blonde under the command of Captain George Anson Byron, 7th Baron Byron. The HMS Blonde arrived in the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands on May 6, 1825.
King Kamehameha II’s brother-in-law William Pitt Kalanimoku, a High Chief who functioned similarly to a prime minister, had been notified of the deaths, and so Hawaiian royalty and nobility gathered at his house where the bodies were moved for the funeral. On May 11, 1825, a state funeral was held for the late King and Queen, the first Christian memorial service for a ruler of Hawaii. The crew from the HMS Blonde participated in the formal procession from the ship to the funeral site, the chaplain of the HMS Blonde said an Anglican prayer, and an American missionary said a prayer in the Hawaiian language.
In the background, the Royal Mausoleum, Mauna ʻAla, now a chapel; Credit – Wikipedia
A Western-style mausoleum was constructed for King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu near the ʻIolani Palace in Honolulu. The mausoleum was a small house made of coral blocks with a thatched roof. King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu were interred there on August 23, 1825. Over time, as more coffins were added, the small vault became crowded. In 1863, construction began on Mauna ʻAla (Fragrant Hills), the Royal Mausoleum of Hawaii in Honolulu. On October 30, 1865, the remains of past deceased royals, including King Kamehameha II and Queen Kamāmalu, were transferred in a torchlit ceremony at night to the new mausoleum. On November 9, 1887, after the Royal Mausoleum became too crowded, the caskets of the members of the House of Kamehameha were moved to the newly built Kamehameha Tomb, an underground vault, under the Kamehameha Dynasty Tomb. Two additional underground vaults were built over the years. In 1922, the Royal Mausoleum, Mauna ʻAla was converted to a chapel after the last royal remains were moved to tombs constructed on the grounds.

Kamehameha Dynasty Tomb – Royal Mausoleum, Honolulu, Hawai; Credit – By Daderot. – Self-photographed, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1101293

Inscriptions of Queen Consorts of Hawaii on the Kamehameha Dynasty Tomb; Credit – www.findagrave.com
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Flantzer, Susan. (2024). Kamehameha II, King of the Hawaiian Islands. Unofficial Royalty. https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/kamehameha-ii-king-of-the-hawaiian-islands/
- U.S. Department of the Interior. Liholiho (Kamehameha II). National Parks Service. https://www.nps.gov/puhe/learn/historyculture/kamehameha2.htm
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Kalākua Kaheiheimālie. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kal%C4%81kua_Kaheiheim%C4%81lie
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Kamāmalu. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kam%C4%81malu
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024). Kamehameha II. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kamehameha_II
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Royal Mausoleum (Mauna ʻAla). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Mausoleum_(Mauna_%CA%BBAla)
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Hawaiian Kingdom. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hawaiian_Kingdom








