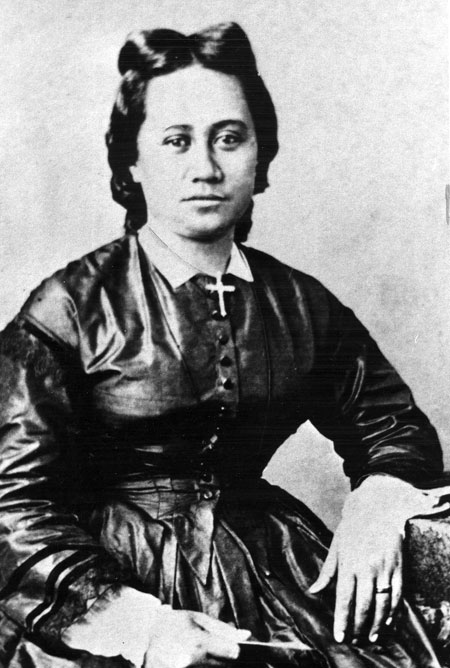by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2024

Margarete Gertrud von der Schulenburg; Credit – kleio.org
The early kings from the British House of Hanover did not publicize their illegitimate children. King George I had three illegitimate daughters with his long-term mistress, Melusine von der Schulenburg, before he became King of Great Britain. At the time of Anna Luise Sophie’s birth, her father, the future King George I of Great Britain, was the heir of his father, Ernst August, Elector of Hanover, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Prince of Calenberg. George succeeded to those titles when his father died in 1698.

Margrete Gertrud’s father, King George I of Great Britain; Credit – Wikipedia
The British House of Stuart failed to provide a legitimate Protestant heir as required by the Act of Settlement of 1701. When Queen Anne of Great Britain died on August 1, 1714, George, Elector of Hanover, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Prince of Calenberg, was the closest Protestant heir to the British throne. George’s mother was Sophia of the Palatinate, commonly called Electress Sophia of Hanover. Sophia was the daughter of Elizabeth Stuart, the second child and eldest daughter of King James VI of Scotland/King James I of England. Therefore, the Protestant, German-born George, Elector of Hanover, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Prince of Calenberg, became King George I of Great Britain, the first monarch of the British House of Hanover, bypassing dozens of Catholics with a better hereditary claim to the British throne.
Margarete Gertrud von der Schulenburg was born on January 10, 1701, in the Electorate of Hanover, now in the German state of Lower Saxony, the daughter of the future King George I of Great Britain and his mistress Melusine von der Schulenburg. Her paternal grandparents were Ernst August, Elector of Hanover, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and Sophia of the Palatinate. Her maternal grandparents were Gustavus Adolphus, Freiherr (Baron) von der Schulenburg (link in German) and his first wife, Petronella Ottilie von Schwencken.

Margarete Gertrud’s mother Melusine von der Schulenburg; Credit – Wikipedia
Margarete Getrud’s mother, Melusine von der Schulenburg, came from an old Brandenburg noble family. Her father served as a member of the Brandenburg Privy Council. Melusine’s mother died in childbirth along with her last child. In 1690, Melusine became a maid of honor to Electress Sophia of Hanover, the mother of the future King George I. A year later, Melusine became George’s mistress. In 1694, George annulled his marriage to Sophia Dorothea of Celle after she fell in love with the Swedish Count Philip Christoph von Königsmarck, an officer in the Hanoverian army. Königsmarck disappeared, and it was widely believed that George ordered Königsmarck’s death. Sophia Dorothea was banished to the Castle of Ahlden in her father’s territory of the Principality of Celle, now in Lower Saxony, Germany. She was not allowed to remarry, would never again see her children, and was kept as a prisoner at the Castle of Ahlden until she died in 1727. George did not marry again, and Melusine remained his mistress until he died, also in 1727.
Margarete Gertrud had two full sisters:
- Anna Luise Sophie von der Schulenburg (1692 – 1773), married Ernst August Philipp von dem Bussche zu Ippenburg, no children, divorced
- Petronilla Melusina von der Schulenburg (1693 – 1778), known as Melusina, married Philip Stanhope, 4th Earl of Chesterfield, no children
Margarete Gertrud had two half-siblings from her father’s marriage to Sophia Dorothea of Celle:
- King George II of Great Britain (1683 – 1760), married Caroline of Ansbach, had eight children
- Sophia Dorothea of Hanover (1687 – 1757), married Friedrich Wilhelm, Margrave of Brandenburg (later King Friedrich Wilhelm I in Prussia), had fourteen children
Margarete Gertrud and her sisters, Petronilla Melusina and Anna Luise Sophie, were never openly acknowledged as King George I’s children. Instead, two of their mother’s sisters and their husbands officially acknowledged them. Anna Luise and Melusina were raised by Melusine’s sister Margarete Gertrud and her husband and distant cousin Friedrich Achaz von der Schulenburg. Margarete was raised by Melusine’s sister Sophie Juliane and her husband Rabe Christoph, Count (Graf) von Oeynhausen. Sometimes Margarete Gertrud is referred to as Margarete Gertrud von Oeynhausen.
In 1714, King George I made his state entry into London accompanied by his mistress Melusine von der Schulenburg, nicknamed “the Maypole” by the British because of her tall, thin appearance. Melusine and their daughters lived with King George I in the royal palaces and Melusine acted as his hostess. At Kensington Palace, Melusine had a three-story apartment overlooking the gardens. Melusine became a naturalized British citizen in 1716 and in the same year was created Duchess of Munster, Countess and Marchioness of Dungannon, and Baroness of Dundalk for life. In 1719, she was further created Duchess of Kendal, Countess of Feversham, and Baroness of Glastonbury and Somerset for life.

Margarete Gertrud’s husband Albrecht Wolfgang, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe; Credit – Wikipedia
Nicknamed Trundchen, Margarete Gertrud was the favorite of her father King George I. At her father’s court, she met the future Albrecht Wolfgang, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe. Albrecht Wolfgang and his brother were educated in England because of their parents’ estrangement and eventual divorce. In 1720, Albrecht Wolfgang entered King George I’s service at court. King George I thought Albrecht Wolfgang would be a good match for Margarete Gertrud.
Before the couple married in 1721, King George I asked Holy Roman Emperor Karl VI to grant Margarete Gertrud an imperial title so her marriage to Albrecht Wolfgang would be an equal marriage. Karl VI agreed and created Margarete Gertrud, the Countess of Oeynhausen. It was also a political marriage. The County of Schaumburg-Lippe bordered the Electorate of Hanover, and King George I was also the Elector of Hanover. The marriage allied the County of Schaumburg-Lippe with George I, thereby neutralizing any territorial expansion of the Electorate of Hanover and providing the small County of Schaumburg-Lippe protection against claims of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel. There was a clause in the marriage contract that King George I would defend the County of Schaumburg-Lippe against its enemies.

Margarete Gertrud and Albrecht Wolfgang’s son Wilhelm, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe; Credit – Wikipedia
Margarete Gertrud and Albrecht Wolfgang had two sons:
- Georg Wilhelm of Schaumburg-Lippe (1722 – 1742), unmarried, killed in a duel at age 20
- Wilhelm, Count of Schaumburg-Lippe (1724 – 1777), married Marie Barbara Eleonore of Lippe-Biesterfeld, had two children who both died young. Wilhelm was an important military commander in the Seven Years’ War. He was General of the Artillery of the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg and a British Field Marshal, the highest rank in the British Army.

The Princely Mausoleum at the St. Martini Church; Credit – Von Beckstet – Eigenes Werk, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=9678304
Twenty-five-year-old Margarete Gertrud died from tuberculosis in Mannheim, then in the Electorate of the Palatinate, now in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, on April 8, 1726, two years before her husband became the Sovereign Count of Schaumburg-Lippe. She was buried in the Princely Mausoleum at the St. Martini Church (links in German) in Stadthagen, then in the County of Schaumburg-Lippe, now in the German state of Lower Saxony.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Autoren der Wikimedia-Projekte. (2005). Graf von Schaumburg-Lippe-Bückeburg. Wikipedia.org; Wikimedia Foundation, Inc. https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Albrecht_Wolfgang_(Schaumburg-Lippe)
- Beauclerk-Dewar, Peter & Powell, Roger. (2006). Right Royal Bastards – The Fruits of Passion. Burke’s Peerage & Gentry LLC.
- Flantzer, Susan. (2015). King George I of Great Britain. Unofficial Royalty. https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/king-george-i-of-great-britain/
- Flantzer, Susan. (2020). Melusine von der Schulenburg, Duchess of Kendal, Mistress of King George I of Great Britain. Unofficial Royalty. https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/melusine-von-der-schulenburg-duchess-of-kendal-mistress-of-king-george-i-of-great-britain/
- Margaret Gertrude, Countess of Oeynhausen. Geni_family_tree. (2022). https://www.geni.com/people/Margaret-Gertrude-Countess-of-Oeynhausen/6000000000769944176
- Margarete Gertrud von Oeynhausen (1701-1726) -… (2023). Findagrave.com. https://www.findagrave.com/memorial/35295100/margarete_gertrud_von_oeynhausen
- Melusine von der Schulenburg, Duchess of Kendal. (2024). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melusine_von_der_Schulenburg
- Weir, Alison. (2008). Britain’s Royal Families – The Complete Genealogy. Vintage Books.