by Susan Flantzer © Unofficial Royalty 2019

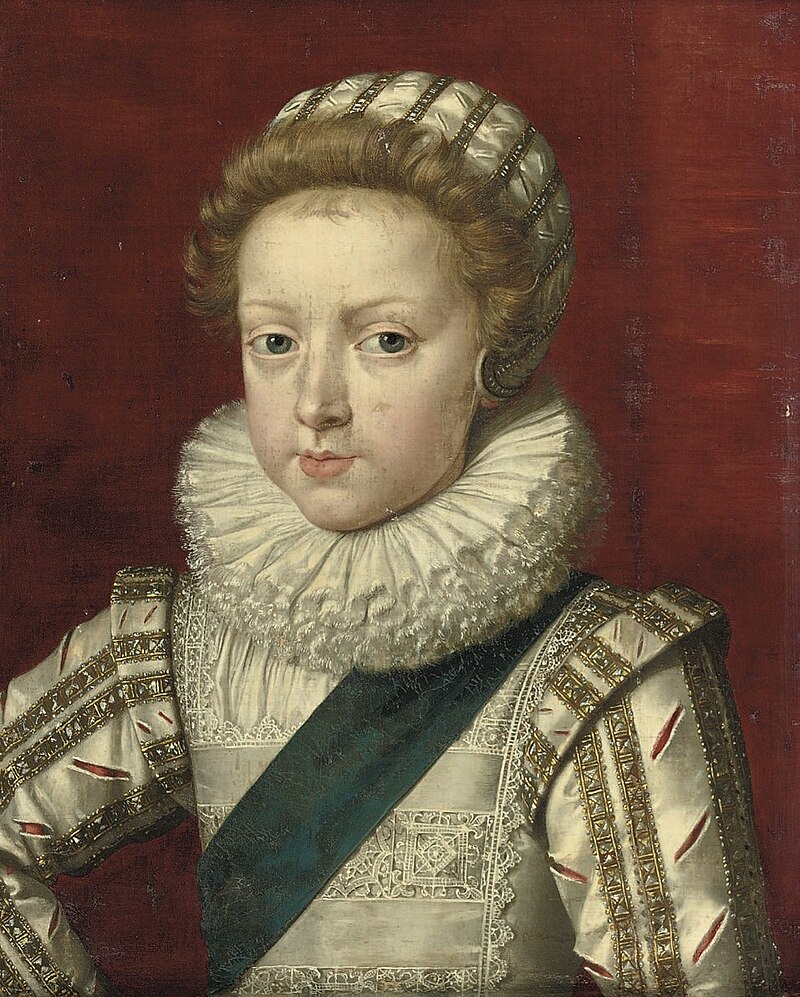
Philippe I, Duke of Orléans; Credit – Wikipedia
Philippe I, Duke of Orléans, the younger son of Louis XIII, King of France and Anne of Austria, Infanta of Spain, was born September 21, 1640, at the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye near Paris. At the time of his birth, he was created Duke of Anjou.
Philippe had one brother:
- Louis XIV, King of France (1638 – 1715), married (1) Maria Theresa of Austria, Infanta of Spain, had six children but only one survived childhood (2) Françoise d’Aubigné, Marquise de Maintenon, morganatic marriage, no children

Philippe and his brother Louis; Credit – Wikipedia
Along with his elder brother Louis, Philippe was raised by the royal governess Françoise de Souvré, Marquise de Lansac until 1643, when Marie-Catherine de Senecey took over. Philippe’s father King Louis XIII died in 1643 and his five-year-old brother then began his 72-year reign as King Louis XIV.
Prime Minister Cardinal Jules Mazarin and Philippe’s mother Queen Anne feared that Philippe would become a source of conflict and harm his brother’s power just as Gaston, Duke of Orléans had done to his brother King Louis XIII. As a result, Philippe was raised “as a girl” to make him effeminate and weak, the total opposite of his brother King Louis XIV. He was treated and dressed like a girl, showered with jewelry and clothes with any masculine behavior deliberately suppressed. Philippe was well educated by tutors chosen by Cardinal Mazarin, emphasizing languages, history, literature, mathematics, and dancing. In 1660, after his uncle Gaston, Duke of Orléans died, Philippe was created Duke of Orléans.
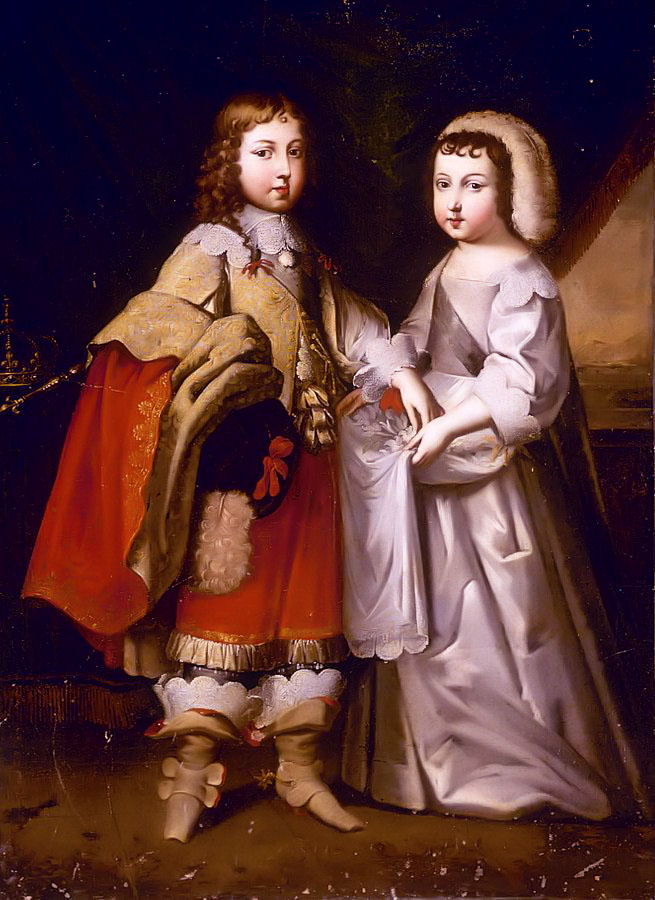

Louis XIV (right) with his brother Philippe (left); Credit – Wikipedia
During the English Civil War (1642–1651), Philippe’s paternal aunt Henrietta Maria, wife of King Charles I of England, and her youngest child and Philippe’s first cousin Henrietta (born 1644) sought refuge at the French court. Mother and daughter were given apartments at the Palais du Louvre, the use of the Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, and a pension, much of which was given to King Charles I in England and to royalist exiles in France. In January 1649, King Charles I was beheaded, and Henrietta and her mother moved to the Palais Royal with her cousins King Louis XIV and Philippe, Duke of Orléans, and their mother.
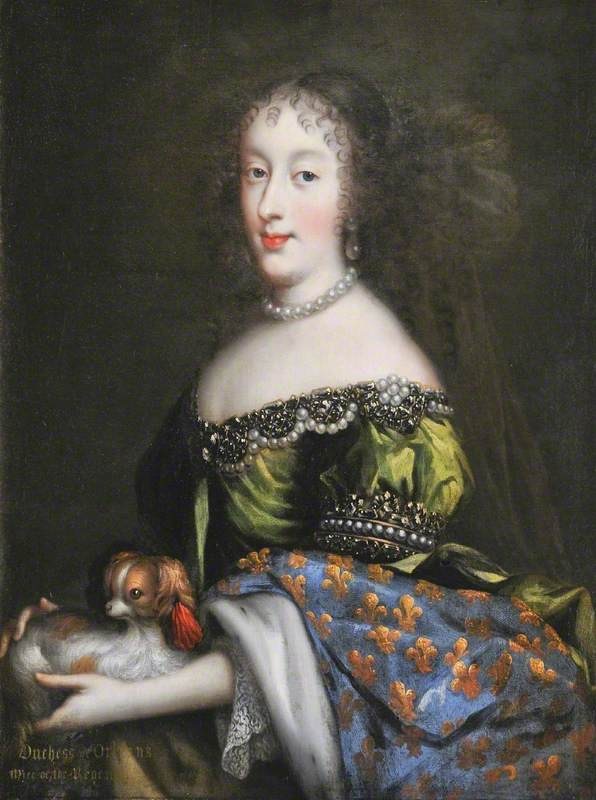

Henrietta of England, Philippe’s first wife; Credit – Wikipedia
Henrietta Maria wanted her daughter to marry her cousin King Louis XIV but his mother did not favor the marriage. Instead, Louis XIV married Maria Theresa of Spain, another first cousin, in 1660. Also in 1660, the monarchy was restored in England and Henrietta’s eldest brother became King Charles II. Now that Henrietta was the sister of the English king, her cousin Philippe became interested in marrying her. Philippe had homosexual affairs but apparently, he was intent on fulfilling his dynastic responsibility of having children. The cousins married on April 1, 1661, and moved into the Palais des Tuileries. Although Philippe and Henrietta had three children, the paternity of the children was doubted by some members of the court as Henrietta had affairs, including an affair with her husband’s lover Guy Armand de Gramont, Comte de Guiche.
Today’s Jacobite claim to the British throne goes through Philippe and Henrietta’s younger daughter Anne Marie. Through her mother, Anne Marie was a granddaughter of King Charles I of England. When Charles Edward Stuart (Bonnie Prince Charlie) and his brother Cardinal Henry Stuart died without legitimate issue, Anne Marie’s descendants inherited the Jacobite claim.
Philippe and Henrietta’s children:
- Marie Louise of Orléans (1662 – 1689), married Carlos II, King of Spain, no children
- Philippe Charles of Orléans, Duke of Valois (1664 – 1666), died in early childhood
- Anne Marie of Orléans (1669 – 1728), married Vittorio Amadeo II, King of Sardinia, had five children
On June 30, 1670, Henrietta died at the age of 26. There were rumors that her husband’s lover Philippe, Chevalier de Lorraine had poisoned her. She was buried at the Basilica of St. Denis near Paris, the burial site of the Kings of France and their families. While Henrietta was mourned at the French court, she was not mourned by her husband due to their strained relationship. Philippe’s brother King Louis XIV wanted a male heir to continue the Orléans line and looked for a second wife for Philippe himself.
King Louis XIV rejected many potential second brides for his brother before settling on the Protestant Princess Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate, known as Liselotte. She was the only daughter of Karl I Ludwig, Elector Palatine and Charlotte of Hesse-Kassel. Liselotte’s paternal grandmother was Elizabeth Stuart, daughter of King James I of England and granddaughter of Mary, Queen of Scots. Liselotte converted to Roman Catholicism and married Philippe on November 19, 1671, at Saint Etienne Cathedral in Châlons, France.

Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate, known as Liselotte, Philippe’s second wife; Credit – Wikipedia
Liselotte acted as a mother to Philippe’s children by Henrietta and maintained correspondence with them throughout their lives. Philippe and Liselotte had three children:
- Alexandre Louis d’Orléans, Duke of Valois (1673 – 1676), died in childhood
- Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (1674 – 1723) married his cousin Françoise Marie de Bourbon, a legitimized daughter of King Louis XIV and one of his mistresses Françoise-Athénaïs de Rochechouart de Mortemart, Marquise of Montespan, had eight children
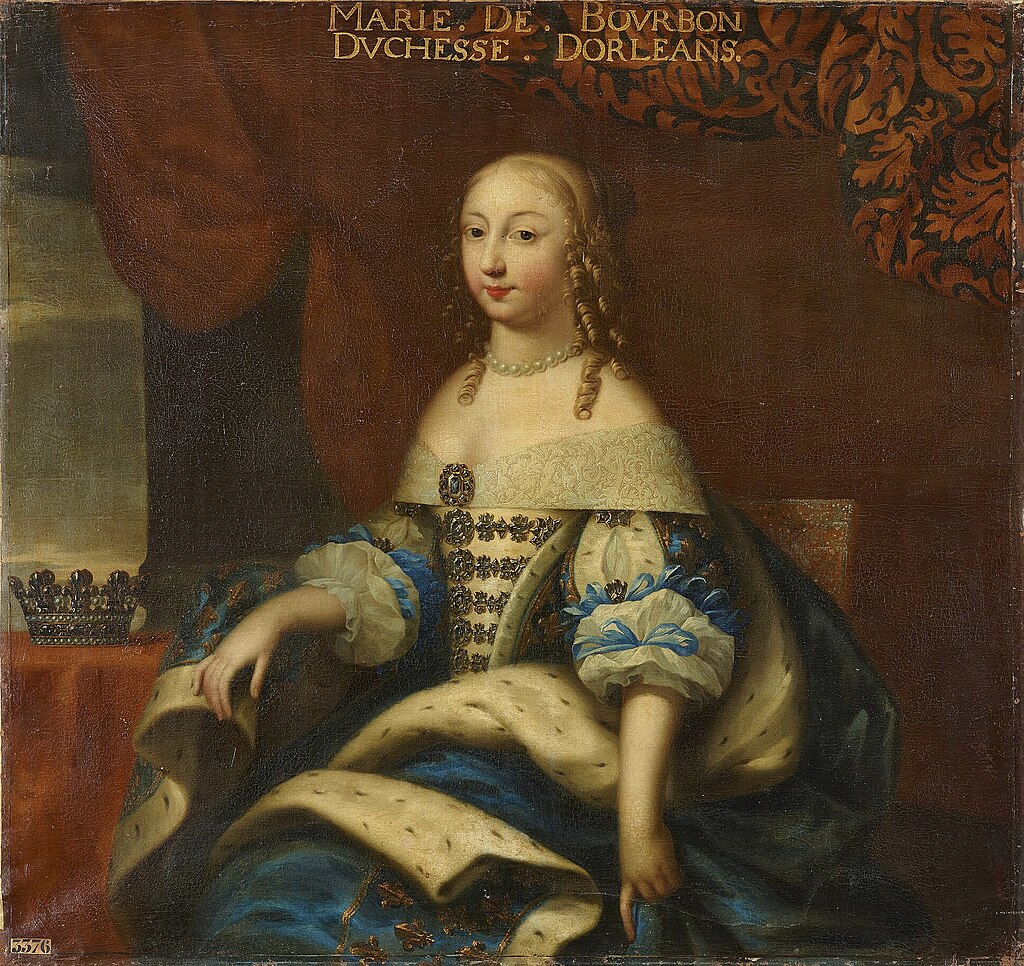
- Élisabeth Charlotte d’Orléans (1676 – 1744) married Leopold, Duke of Lorraine, had thirteen children, were the grandparents of Marie Antoinette, Queen of France

Liselotte with her two surviving children; Credit – Wikipedia
Philippe’s careful investment and management of his various estates made him a wealthy man, and his wealth greatly increased when he inherited the fortune of his extremely wealthy paternal first cousin Anne Marie Louise of Orléans, Duchess of Montpensier upon her death in 1693. Philippe is acknowledged as the biological and financial founder of the House of Orléans. In his later life, Philippe maintained his lavish lifestyle easily and he found much satisfaction in the activities of his children and grandchildren.
On June 9, 1701, Philippe I, Duke of Orléans died from a stroke at the Château de Saint-Cloud at the age of 60. He was buried at the Basilica of St. Denis, near Paris. His wife Liselotte survived Philippe by twenty-one years, dying at the Château de Saint-Cloud at age 70 on December 8, 1722.
Philippe’s descendants include King Felipe VI of Spain, King Philippe of the Belgians, Grand Duke Henri of Luxembourg, Henri, Count of Paris, the Orléanist pretender to the French throne, and Victor Emmanuel of Savoy, the pretender to the Italian throne.

Basilica of St. Denis; Credit – By Thomas Clouet – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=42109690
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- De.wikipedia.org. (2018). Philippe I. de Bourbon, duc d’Orléans. [online] Available at: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philippe_I._de_Bourbon,_duc_d%E2%80%99Orl%C3%A9ans [Accessed 29 Oct. 2018].
- En.wikipedia.org. (2018). Philippe I, Duke of Orléans. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philippe_I,_Duke_of_Orl%C3%A9ans [Accessed 29 Oct. 2018].
- Fr.wikipedia.org. (2018). Philippe d’Orléans (1640-1701). [online] Available at: https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philippe_d%27Orl%C3%A9ans_(1640-1701) [Accessed 29 Oct. 2018].
- Fraser, Antonia. (2006). Love and Louis XIV. New York: Nan A. Talese Doubleday.