by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2023
The Holy Roman Empire was a limited elective monarchy composed of hundreds of kingdoms, principalities, duchies, counties, prince-bishoprics, and Free Imperial Cities in central Europe. The Holy Roman Empire was not really holy since, after Holy Roman Emperor Charles V in 1530, no emperors were crowned by the pope or a bishop. It was not Roman but rather German because it was mainly in the regions of present-day Germany and Austria. It was an empire in name only – the territories it covered were mostly independent each with its own rulers. The Holy Roman Emperor directly ruled over only his family territories, and could not issue decrees and rule autonomously over the Holy Roman Empire. A Holy Roman Emperor was only as strong as his army and alliances, including marriage alliances, made him, and his power was severely restricted by the many sovereigns of the constituent monarchies of the Holy Roman Empire. From the 13th century, prince-electors, or electors for short, elected the Holy Roman Emperor from among the sovereigns of the constituent states.
Frequently but not always, it was common practice to elect the deceased Holy Roman Emperor’s heir. The Holy Roman Empire was an elective monarchy. No person had a legal right to the succession simply because he was related to the current Holy Roman Emperor. However, the Holy Roman Emperor could and often did, while still alive, have a relative (usually a son) elected to succeed him after his death. This elected heir apparent used the title King of the Romans.
- Learn more at Unofficial Royalty: What was the Holy Roman Empire?
********************

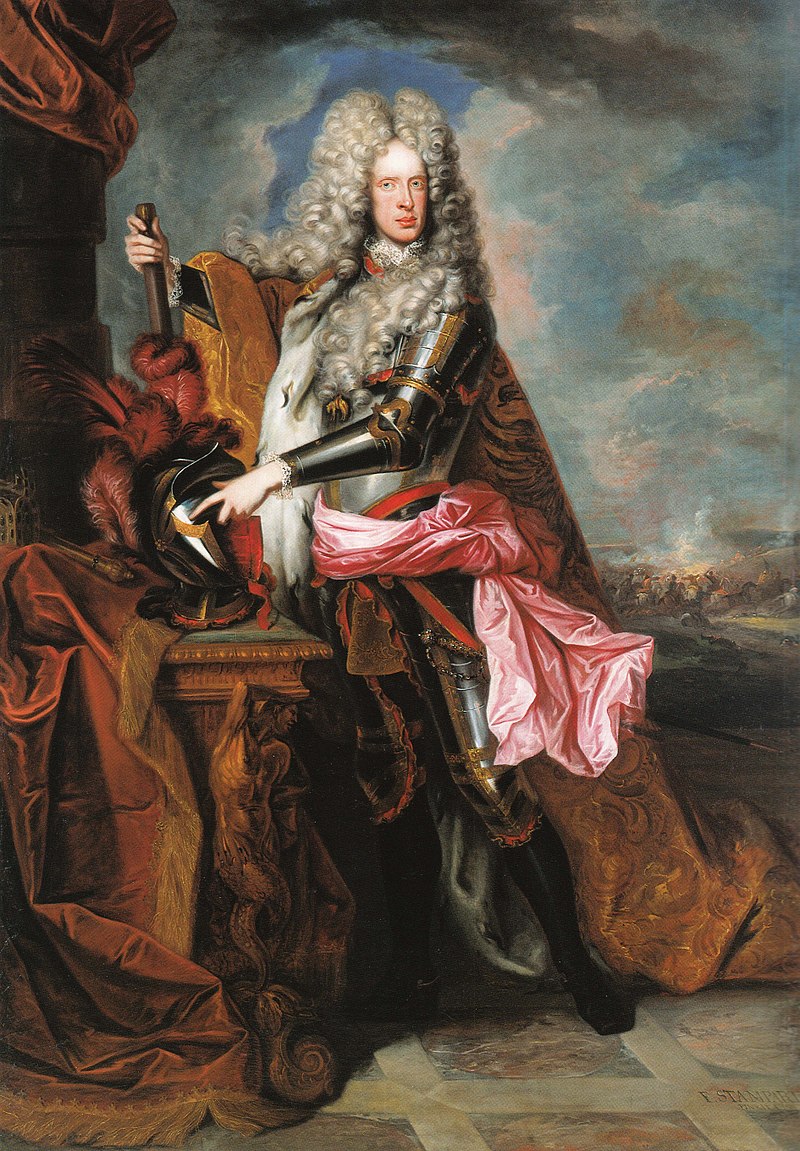
Karl VII, Holy Roman Emperor; Credit – Wikipedia
Reigning as Karl VII, Holy Roman Emperor from 1742 – 1745 and as Karl I, Prince-Elector of Bavaria from 1726 – 1745, Karl Albrecht was born on August 6, 1697, in Brussels, then in the Duchy of Brabant, now in Belgium. His reign as Holy Roman Emperor marked the end of three centuries of the House of Habsburg’s rule as Holy Roman Emperors. Karl was the second of the nine children and the eldest of the eight sons of Maximilian II Emanuel, Prince-Elector of Bavaria and his second wife Teresa Kunegunda Sobieska. His paternal grandparents were Ferdinand Maria, Elector of Bavaria and Princess Henriette Adelaide of Savoy. Karl’s maternal grandparents were Jan III Sobieski, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania and Marie Casimire Louise de La Grange d’Arquien, a French noblewoman
Karl had eight siblings:
- Princess Maria Anna Karoline of Bavaria (1696 – 1750), a nun
- Prince Philip Moritz Maria of Bavaria (1698 – 1719), unmarried, died in his twenties
- Prince Ferdinand Maria of Bavaria, Imperial Field Marshal (1699 – 1738), married Countess Palatine Maria Anna of Neuburg, had two sons
- Prince Clemens August of Bavaria, Archbishop of Cologne, Prince-Bishop of Hildesheim, Bishop of Paderborn (1700 – 1761)
- Prince Wilhelm of Bavaria (1701 – 1704), died in childhood
- Prince Alois Johann Adolf of Bavaria (1702 – 1705), died in childhood
- Prince Johann Theodor of Bavaria, Cardinal, Prince-Bishop of Regensburg, Bishop of Freising, Bishop of Liège (1703 – 1763)
- Prince Maximilian Emanuel Thomas of Bavaria (1704 – 1709), died in childhood
Karl had three half-brothers from his father’s first marriage to Maria Antonia of Austria, daughter of Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor but none survived childhood. Maria Antonia died in childbirth delivering her last son. Because Maria Antonia’s mother Margarita Teresa of Spain (died 1673) was the eldest sister of the childless Carlos II, King of Spain who had had physical and mental conditions probably caused by the continued inbreeding of the House of Habsburg, her son Joseph Ferdinand of Bavaria was a claimant to the throne of Spain after Carlos’ death in 1700. Joseph Ferdinand died suddenly at the age of six after suffering seizures, vomiting, and loss of consciousness. He was rumored to have been poisoned which is very possible due to his close connection to the Spanish throne. The fight for the throne of Spain caused the War of the Spanish Succession, a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1715.
- Prince Leopold Ferdinand of Bavaria (born and died 1689)
Prince Anton of Bavaria (born and died 1690) - Prince Joseph Ferdinand of Bavaria (1692 – 1699)

A young Karl, circa 1717 – 1719; Credit – Wikipedia
Karl had been born in Brussels because his father was Governor-General of the Habsburg Netherlands. In 1701, the family returned to Bavaria. Bavaria fought against the Holy Roman Empire during the War of the Spanish Succession, Karl’s father Maximilian II Emanuel, Prince-Elector of Bavaria, who had served the Holy Roman Emperor as Governor-General of the Habsburg Netherlands was exiled from any territories of the Holy Roman Empire. Karl and his siblings remained in Bavaria and his mother acted as Regent for her husband. In May 1705, after a stay in Venice, the Austrian authorities refused to allow Karl’s mother to return to Bavaria and forced her into exile in Venice, which lasted ten years.
In 1706, Karl and the three eldest of his brothers were taken to Klagenfurt, Austria on the orders of Holy Emperor Joseph I where they were taught and brought up by Jesuit priests. Karl’s sister and his two youngest brothers remained with their mother. The family was not reunited until the Spanish War of Succession ended in 1715. From December 1715 to August 1716, Karl took an educational tour of Italy. In 1717, he served with the Bavarian army on the Austrian side in the Austro-Turkish War.

Karl’s wife Archduchess Maria Amalie of Austria; Credit – Wikipedia
On October 5, 1722, Karl married Archduchess Maria Amalie of Austria, whom he had met at the imperial court in Vienna. Maria Amalie was the younger of the two daughters of Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor who had died in 1711 and Wilhelmine Amalie of Brunswick-Lüneburg. Karl thought that a marriage with the House of Habsburg would widen his dynastic and economic prospects.

Two of Karl’s children, his successor Maximilian III Joseph, Elector of Bavaria and Joseph Ludwig; Credit – Wikipedia
Karl and Maria Amalie had seven children but only four survived to adulthood:
- Princess Maximiliana Maria of Bavaria (born and died 1723)
- Princess Maria Antonia of Bavaria (1724 – 1780), married Friedrich Christian, Elector of Saxony, had eight children
- Princess Theresa Benedicta of Bavaria (1725 – 1743), died in her teens from smallpox
- Maximilian III Joseph, Elector of Bavaria (1727 – 1777), married Maria Anna Sophia of Saxony, no children
- Prince Joseph Ludwig of Bavaria (1728 – 1733), died in childhood
- Princess Maria Anna Josepha of Bavaria (1734 – 1776), married Ludwig Georg, Margrave of Baden-Baden, no children
- Princess Maria Josepha of Bavaria (1739 – 1767), married her second cousin Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, no children

Nymphenburg Palace; Credit – By Richard Bartz, Munich aka Makro Freak – Own work, CC BY-SA 2.5, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4083697
In 1726, after the death of his father, Karl became Elector of Bavaria. He maintained good relations with both the Habsburgs and France, continuing his father’s policies. Karl and his family lived at Nymphenburg Palace in Munich.
In 1711, Karl’s father-in-law Holy Roman Emperor Joseph I died suddenly from smallpox. Joseph I had three children but his only son died from hydrocephalus before his first birthday. His two daughters were Archduchess Maria Josepha of Austria and Karl’s wife Archduchess Maria Amalie of Austria. Upon the sudden death of his elder brother Joseph I, Archduke Karl of Austria automatically succeeded to the Habsburg hereditary lands and was elected Karl VI, Holy Roman Emperor. However, Karl VI also had a succession problem. He had one son who died in infancy and three daughters, with one daughter dying in childhood.
Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I had devised the Mutual Pact of Succession, a succession device. The Mutual Pact of Succession stated that the Habsburg hereditary lands would be inherited by the respective male heirs of his sons, the future Holy Roman Emperor Joseph I, and the future Holy Roman Emperor Karl VI. If either Joseph I or Karl VI should fail to have a son, the other one would succeed him in all the Habsburg hereditary lands. If both brothers died without sons, the daughters of Joseph I, the elder brother, would have absolute precedence over the daughters of Karl VI, the younger brother, and the eldest daughter of Joseph would ascend to the thrones of all the Habsburg hereditary lands. This meant that Archduchess Maria Josepha of Austria (1699 – 1757), the elder of the two daughters of Holy Roman Emperor Joseph I, would inherit the Habsburg hereditary lands upon the death of her uncle Holy Roman Emperor Karl VI.
However, when Karl VI became Holy Roman Emperor, he amended the Mutual Pact of Succession. Karl VI’s Pragmatic Sanction of 1713 annulled the terms of the Mutual Pact of Succession, making his daughter Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria the heir to the Habsburg hereditary lands instead of his niece Archduchess Maria Josepha. After Karl VI’s death in 1740, his daughter Maria Theresa succeeded to the Habsburg hereditary lands as the Queen of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, Queen of Bohemia, and Archduchess of Austria in her own right, the only female to hold those sovereign positions.
However, as the son-in-law of Holy Roman Emperor Joseph I and brother-in-law of Archduchess Maria Josepha, Karl, Elector of Bavaria rejected the Pragmatic Sanction and claimed the Habsburg hereditary territories against Maria Theresa. With the 1741 Treaty of Nymphenburg, Karl, Elector of Bavaria aligned himself with Spain, France, Prussia, Saxony, and Sardinia against Austria. This led to led to the War of Austrian Succession (1740 – 1748), resulting in the eventual confirmation of Maria Theresa’s Habsburg titles.
While all this was occurring, Karl, Elector of Bavaria was elected Holy Roman Emperor Karl VII in 1742. Karl VII was a member of the House of Wittelsbach, and his reign as Holy Roman Emperor marked the end of three centuries of uninterrupted Habsburg imperial rule. The War of Austrian Succession Karl greatly overshadowed three-year reign as Holy Roman Emperor.

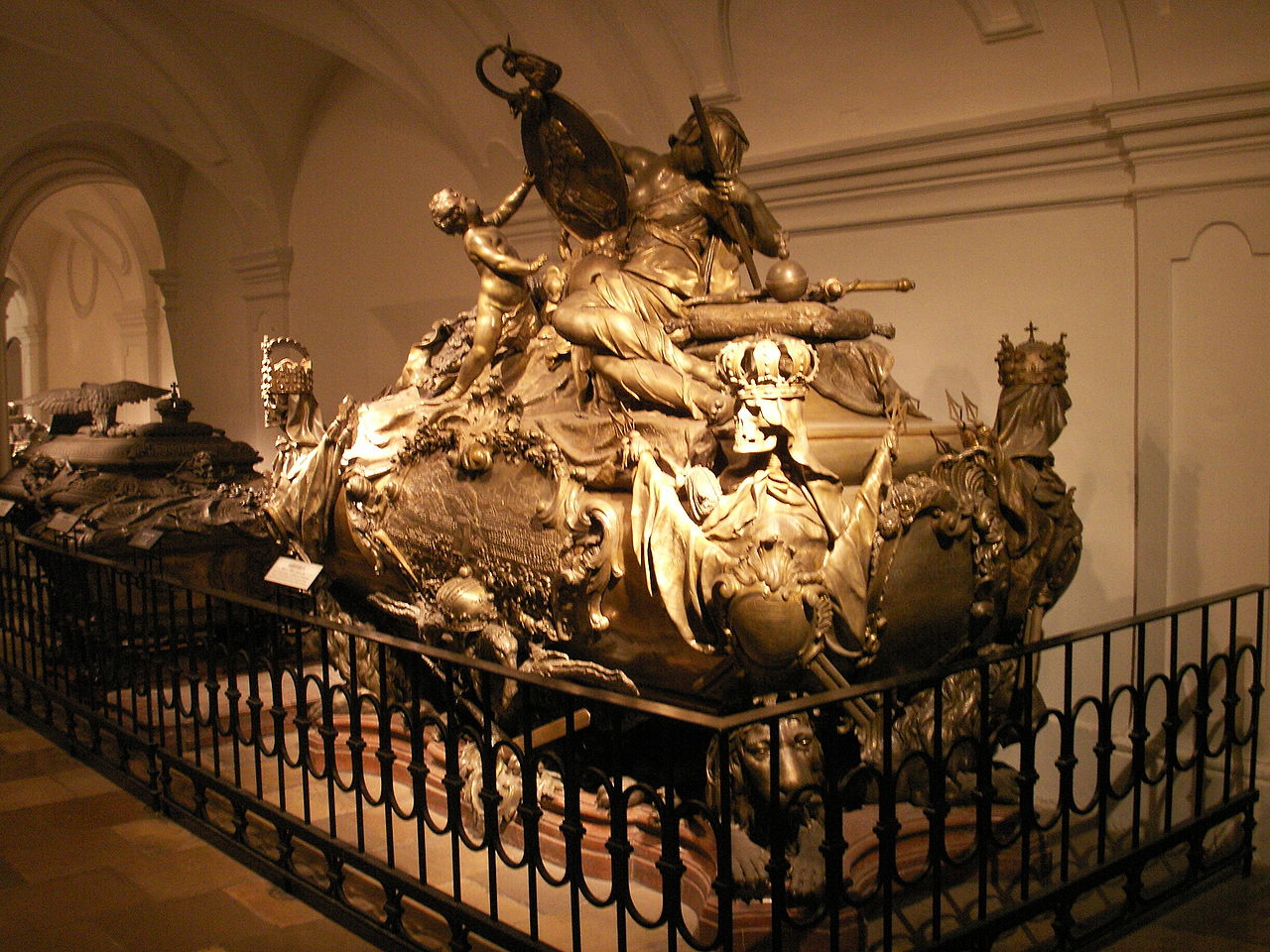
Tomb of Karl VII, Holy Roman Emperor, Elector of Bavaria; Credit – By krischnig – Self-photographed, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12359771
On January 20, 1745, 47-year-old Karl VII, Holy Roman Emperor died at the Munich Residenz in Munich, then in the Electorate of Bavaria, now in the German state of Bavaria. His autopsy report listed gout, kidney stones, and heart problems as contributory factors to his death. He was interred in the Theatinerkirche in Munich. Maria Amalie of Austria, daughter of Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor, survived her husband by nearly thirteen years, dying at Nymphenburg Palace in Munich on December 11, 1756, aged 55. Like her husband, she was buried in the Theatinerkirche in Munich. In keeping with tradition, their hearts were buried separately, at the Chapel of Grace in Altötting, Bavaria, Germany.
On the day of his death, Karl VII, Holy Roman had declared his son Maximilian III Joseph, two months short of his eighteenth birthday, to be of legal age, which enabled him to succeed as Elector of Bavaria without a regent. Maximilian III Joseph, Elector of Bavaria made peace with Austria via the 1745 Treaty of Füssen. Bavaria recognized the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713. Maximilian III Joseph, Elector of Bavaria promised to support the candidacy of Francis Stephen of Lorraine, the husband of Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria and future Habsburgs, as Holy Roman Emperor. Austria did not demand any reparations and recognized the legitimacy of Karl VII’s election as Holy Roman Emperor.

Maria Theresa, Archduchess of Austria, and Queen of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia in her own right; Credit – Wikipedia
As for Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria, since only a male could be Holy Roman Emperor, she arranged for her husband Francis Stephen, Duke of Lorraine to be elected Holy Roman Emperor. Despite the snub for being a female, Maria Theresa wielded the real power. The last four Holy Roman Emperors were her husband who reigned as Franz I, Holy Roman Emperor, her two sons Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor and Leopold II, Holy Roman Emperor, and her grandson Franz II, Holy Roman Emperor.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Charles VII, Holy Roman Emperor (2023) Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_VII,_Holy_Roman_Emperor (Accessed: 31 August 2023).
- Flantzer, Susan. (2013) Maria Theresa, Archduchess of Austria, and Queen of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia, Unofficial Royalty. Available at: https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/may-13-daily-featured-royal-date/ (Accessed: 31 August 2023).
- Karl VII. (HRR) (2023) Wikipedia (German). Available at: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karl_VII._(HRR) (Accessed: 31 August 2023).
- Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria (2023) Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maximilian_II_Emanuel,_Elector_of_Bavaria (Accessed: 31 August 2023).
- Wheatcroft, Andrew. (1995) The Habsburgs. London: Viking.
- Wilson, Peter H. (2016) Heart of Europe – A History of the Holy Roman Empire. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.