by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2023

Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor; Credit – Wikipedia
The Holy Roman Empire was a limited elective monarchy composed of hundreds of kingdoms, principalities, duchies, counties, prince-bishoprics, and Free Imperial Cities in central Europe. The Holy Roman Empire was not really holy since, after Holy Roman Emperor Charles V in 1530, no emperors were crowned by the pope or a bishop. It was not Roman but rather German because it was mainly in the regions of present-day Germany and Austria. It was an empire in name only – the territories it covered were mostly independent each with its own rulers. The Holy Roman Emperor directly ruled over only his family territories, and could not issue decrees and rule autonomously over the Holy Roman Empire. A Holy Roman Emperor was only as strong as his army and alliances, including marriage alliances, made him, and his power was severely restricted by the many sovereigns of the constituent monarchies of the Holy Roman Empire. From the 13th century, prince-electors, or electors for short, elected the Holy Roman Emperor from among the sovereigns of the constituent states.
Frequently but not always, it was common practice to elect the deceased Holy Roman Emperor’s heir. The Holy Roman Empire was an elective monarchy. No person had a legal right to the succession simply because he was related to the current Holy Roman Emperor. However, the Holy Roman Emperor could and often did, while still alive, have a relative (usually a son) elected to succeed him after his death. This elected heir apparent used the title King of the Romans.
Learn more at Unofficial Royalty: What was the Holy Roman Empire?
********************
Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor (reigned 1556 – 1564), King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia (reigned 1526 – 1564), Archduke of Austria (reigned 1521 – 1564) was born at the Archiepiscopal Palace of Alcalá de Henares in Alcalá de Henares, Kingdom of Castile, now in Spain, on March 10, 1503. He was the fourth of the six children and the second of the two sons of Philip of Austria, Duke of Burgundy, the ruler of the vast and wealthy Burgundian State from the House of Habsburg, and Juana I, Queen of Castile and León from the House of Trastámara. Ferdinand’s paternal grandparents were Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor and the ruler of the Archduchy of Austria, and the Duchies of Styria, Carinthia, and Carniola, and the first of his three wives, Mary, Duchess of Burgundy, the ruler of the Burgundian State in her own right. His maternal grandparents were Ferdinand II, King of Aragon and Isabella I, Queen of Castile and León.

A portrait of the extended Habsburg family: standing (left to right) Maximilian I. Holy Roman Emperor; Maximilian I’s son Philip of Austria; Maximilian I’s first wife Mary of Burgundy; sitting (left to right) Maximilian I and Mary’s grandsons Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor and Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor; and Louis II, King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia, the husband of Maximilian and Mary’s granddaughter Mary of Austria; (Note: This portrait is anachronistic. Mary of Burgundy died in 1482 when her son Philip of Austria was 4 years old and her son Philip died in 1506 when his son Ferdinand was 4 years old); by Bernhard Strigel painted after 1515; Credit – Wikipedia
Ferdinand had five siblings. His brother was Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain, among many other titles, and his sisters were all queen consorts.
- Eleanor of Austria, Queen of Portugal, Queen of France (1498 – 1558), married (1) Manuel I, King of Portugal (his third wife), had two children (2) François I, King of France (his second wife), no children
- Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, also Carlos I, King of Spain (1500 – 1558), married Isabella of Portugal, had five children including Felipe II, King of Spain
- Isabella of Austria, Queen of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden (1501 – 1526), married Christian II, King of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden, had five children, only two daughters survived childhood
- Mary of Austria, Queen of Bohemia and Hungary, Governor of the Spanish Netherlands (1505 – 1558), married Ludovicus II, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia, the brother of Ferdinand’s wife, no children
- Catherine of Austria, Queen of Portugal (1507 – 1578), married João III, King of Portugal, had nine children

Ferdinand’s parents Philip of Habsburg, Duke of Burgundy and Juana I, Queen of Castile and León; Credit – Wikipedia
Before Ferdinand was seven years old, his father had died and his mother had been declared too mentally ill to reign as Queen of Castile and León and was confined in a convent for the rest of her life. Ferdinand’s father Philip of Habsburg (also known as Philip the Handsome) was the heir to both his father’s and mother’s dominions. His mother Mary, Duchess of Burgundy was the only child of Charles I (the Bold), Duke of Burgundy, ruler of the vast and wealthy Burgundian State (parts of the present-day Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, and Germany), and succeeded him after his death at the Battle of Nancy during the Burgundian Wars in 1477. In March 1482, Philip’s mother Mary, Duchess of Burgundy died from internal injuries received in a horse-riding accident. Philip, who was not quite four years old, succeeded his mother as ruler of the Burgundian State under the guardianship of his father Maximilian.
Philip’s father Maximilian was the son of Friedrich III, Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke of Austria, Duke of Styria, Carinthia, and Carniola, today part of Austria and Slovenia. Maximilian was elected King of the Romans in 1486. The Holy Roman Empire was an elective monarchy. No person had a legal right to the succession simply because he was related to the current Holy Roman Emperor. However, the Holy Roman Emperor could, and often did, have a male relative (usually a son) elected to succeed him after his death. This elected heir apparent bore the title King of the Romans. Maximilian became Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke of Austria, and Duke of Styria, Carinthia, and Carniola when his father Friedrich III, Holy Roman Emperor, Archduke of Austria, Duke of Styria, Carinthia, and Carniola died in 1493. However, Philip predeceased his father Maximilian, and never succeeded to his father’s dominions but his eldest son, Ferdinand’s elder brother, did. Best known as Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor and Carlos I, King of Spain, he was one of the most powerful ever monarchs and had a large number of titles due to his vast inheritance of the Burgundian, Spanish, and Austrian realms.
A year after his birth, Ferdinand’s maternal grandmother Isabella I, Queen of Castile and León died. Ferdinand’s mother Juana became Queen of Castile and León but her father Ferdinand II, King of Aragon proclaimed himself Governor and Administrator of Castile and León. In 1506, Ferdinand’s father Philip became King of Castile and León jure uxoris (by the right of his wife) as Philip I, initiating the rule of the Habsburgs in the Spanish kingdoms which would last until 1700 when the Spanish branch of the House of Habsburg became extinct. However, Philip’s rule lasted only from July 12, 1506 to September 25, 1506, when he died, aged 28, apparently of typhoid fever, although an assassination by poisoning was rumored at the time.
Ferdinand’s father Philip had spread rumors about Juana’s supposed mental illness and her misunderstood behavior after his death may have reinforced these rumors. In 1509, Juana’s father Ferdinand II, King of Aragon convinced the parliament that Juana was too mentally ill to govern, and was appointed her guardian and the regent of Castile and León. Juana was confined in the Royal Convent of Santa Clara in Tordesillas, Castile, now in Spain, under the orders of her father. In 1516, Ferdinand II, King of Aragon died. In his will, Ferdinand named his daughter Juana and her eldest son Charles the co-heirs of the Kingdom of Aragon. However, Juana would never reign as her son Charles would continue keeping her confined. Juana would not be released from her confinement until she died in 1555. Many historians feel that Juana was not mentally ill but had been manipulated by her father, husband, and her son. Juana’s father Ferdinand II, King of Aragon and her son Charles had a lot to gain from Juana being declared unfit to rule and confined.

Ferdinand’s wife Anne of Hungary and Bohemia; Credit – Wikipedia
On May 26, 1521, in Linz, Archduchy of Austria, now in Austria, Ferdinand married Anna of Bohemia and Hungary, daughter of King Vladislaus II of Bohemia and Hungary and his third wife Anne of Foix-Candale. Anna’s mother died due to birth complications shortly after giving birth to her second child, the future Ludovicus II, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia. The death of Anna’s father King Vladislaus II in 1516 left Anna and her brother under the guardianship of the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I. It was arranged for Anna to marry his grandson, then Archduke Ferdinand of Austria. At the time of his marriage in 1521, Ferdinand was governing the Habsburg hereditary lands on behalf of his older brother Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. The marriage contract stipulated that Ferdinand should succeed Anna’s brother Ludovicus as King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia in case Ludovicus died without legitimate male heirs.

Three sons of Ferdinand and Anna: Maximilian and his younger brothers Ferdinand and Johann; Credit – Wikipedia
Similar to the situation with King Louis XVI of France and Marie Antoinette, Ferdinand and Anna at first seemed to suffer from a lack of sexual instruction, but eventually, the marriage proved extremely successful both personally and politically. Ferdinand and Anna had fifteen children and all but two reached adulthood. Sadly, Anna died due to childbirth complications on January 27, 1547, at the age of forty-four, three days after giving birth to her fifteenth child. Despite being encouraged to remarry, Ferdinand could not forget his wife and never remarried.
- Elizabeth of Austria, Queen of Poland (1526 – 1545), married King Sigismund II Augustus of Poland, no children
- Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia (1527 – 1576), married his first cousin Maria of Spain, had sixteen children
- Anna of Austria, Duchess of Bavaria (1528 – 1590), married Albrecht V, Duke of Bavaria, had seven children
- Ferdinand II, Archduke of Austria (1529 – 1595), married (1) Philippine Welser, had four children (2) his niece Anna Caterina Gonzaga, had three daughters
- Maria of Austria, Duchess of Jülich-Cleves-Berg (1531 – 1581), married to Wilhelm, Duke of Jülich-Cleves-Berg, had seven children
- Magdalena of Austria (1532 – 1590), a nun
- Catherine of Austria, Queen of Poland (1533 – 1572), married (1) Francesco III Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, Marquess of Montferrat, no children (2) King Sigismund II Augustus of Poland, no children
- Eleanor of Austria, Duchess of Mantua (1534 – 1594), married Guglielmo Gonzaga I, Duke of Mantua, had three children
- Margarethe of Austria (1536 – 1567), a nun
- Johann of Austria (1538 – 1539), died in infancy
- Barbara of Austria, Duchess of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio (1539 – 1572), married Alfonso II d’Este, Duke of Ferrara, Modena and Reggio, no children
- Karl II, Archduke of Austria (1540 – 1590), his niece Maria Anna of Bavaria, had fifteen children
- Ursula of Austria (1541 – 1543), died in early childhood
- Helena of Austria (1543 – 1574), a nun
- Johanna of Austria, Grand Duchess of Tuscany (1547 – 1578), married Francesco I de’ Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, had eight children, only two daughters survived childhood including Marie de’ Medici, 2nd wife of King Henri IV of France
Ludovicus II, King of Hungary, Croatia, and Bohemia died without a legitimate male heir after he was thrown from his horse at the Battle of Mohács against the Ottoman Empire in 1526. Ferdinand claimed both kingdoms and was elected King of Bohemia later in 1526. Ferdinand was proclaimed King of Hungary by a group of nobles, but another group of Hungarian nobles refused to allow a foreign ruler to hold that title and elected Hungarian John Zápolya as an alternative king. Although this conflict lasted until 1570, Ferdinand had the support of his older brother Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, and was generally recognized as King of Hungary. Additionally, in 1531, Charles V recognized Ferdinand as his successor as Holy Roman Emperor, and Ferdinand was elevated to the title King of the Romans.

Ferdinand’s brother Charles several years before his abdication; Credit – Wikipedia
Physically exhausted after forty years of ruling, Ferdinand’s older brother Charles abdicated in 1555, the same year his 75-year-old mother Juana, confined in a convent for forty-six years, died. Charles retired to the peace of the Monastery of Yuste in Extremadura, Spain where he died in 1558. Upon Charles’s abdication, his younger brother Ferdinand, who had already been given Charles’ Austrian lands in 1521, became the Holy Roman Emperor. The Spanish Empire, including the possessions in the Netherlands, Italy, and the New World, was inherited by Charles’ son who reigned as Felipe II, King of Spain.
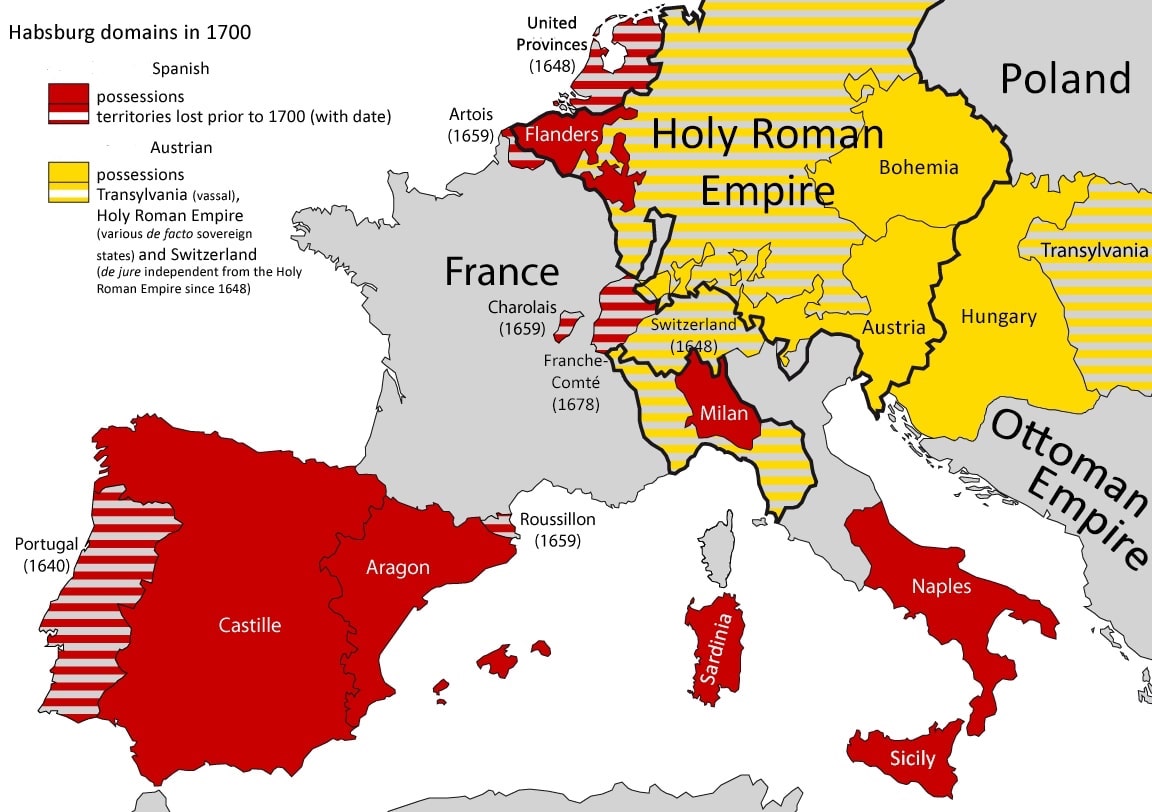
Division of the Habsburg lands after the death of Charles V, Holy Roman Empeor; Credit – By Barjimoa – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=93587376
Unlike his father Maximilian I and his brother Charles V, Ferdinand I did not travel between his domains. In 1533, he had moved his residence to Vienna and spent most of his time there. After Ferdinand became Holy Roman Emperor, Vienna became the capital of the Holy Roman Empire. During his reign as Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand pursued a policy aimed at strengthening peace between the constituent monarchies of the Holy Roman Empire, worked on reaching compromises between Catholics and Protestants, and consolidated imperial forces to fight the Ottoman Empire’s invasion in Central Europe. In December 1562, Ferdinand had his eldest son Maximilian elected King of the Romans, meaning that he would become Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor. In addition, Ferdinand passed the crown of Hungary to his son in 1563.

Funeral of Ferdinand I, Holy Romand Emperor; Credit – Wikipedia
Plagued by fever attacks during the last years of his life, Ferdinand died in Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, now in Austria, on July 25, 1564, aged 61, and was buried next to his wife Anna in St. Vitus Cathedral in Prague, Kingdom of Bohemia, now in the Czech Republic. Their son Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor was buried with his parents.

Tomb of Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor, his wife Anna, and their son Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor; Credit – Wikipedia
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Ferdinand I, Holy Roman Emperor (2023) Wikipedia. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferdinand_I,_Holy_Roman_Emperor (Accessed: 17 May 2023).
- Flantzer, Susan. (2022) Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, King of Spain, Archduke of Austria, Lord of the Netherlands, Duke of Burgundy, Unofficial Royalty. Available at: https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/charles-v-holy-roman-emperor-carlos-i-king-of-spain-karl-i-archduke-of-austria-charles-ii-lord-of-the-netherlands-duke-of-burgundy/ (Accessed: 17 May 2023).
- Flantzer, Susan, 2022. Juana I, Queen of Castile and León and Queen of Aragon. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/juana-i-queen-of-castile-and-leon-and-queen-of-aragon/> [Accessed 17 May 2023].
- Flantzer, Susan, 2022. Philip of Austria, Duke of Burgundy, King of Castile and León. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/philip-of-austria-duke-of-burgundy-king-of-castile/> [Accessed 17 May 2023].
- Wheatcroft, Andrew, 1995. The Habsburgs. London: Viking.
- Wilson, Peter, 2016. Heart of Europe: A History of the Holy Roman Empire. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.

