by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2024
The Hawaiian Islands, located in the Pacific Ocean, were originally divided into several independent chiefdoms. The Kingdom of Hawaii was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great of the independent island of Hawaii, conquered the independent islands of Oahu, Maui, Molokai, and Lanai, and unified them under one government and ruled as Kamehameha I, King of the Hawaiian Islands. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unified when Kauai and Niihau voluntarily joined the Kingdom of Hawaii. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua.
In 1778, British explorer James Cook visited the islands. This led to increased trade and the introduction of new technologies and ideas. In the mid-19th century, American influence in Hawaii dramatically increased when American merchants, missionaries, and settlers arrived on the islands. Protestant missionaries converted most of the native people to Christianity. Merchants set up sugar plantations, and the United States Navy established a base at Pearl Harbor. The newcomers brought diseases that were new to the indigenous people, including influenza, measles, smallpox, syphilis, tuberculosis, and whooping cough. At the time of James Cook’s arrival in 1778, the indigenous Hawaiian population is estimated to have been between 250,000 and 800,000. By 1890, the indigenous Hawaiian population had declined to less than 40,000.
In 1893, a group of local businessmen and politicians composed of six non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects, five American nationals, one British national, and one German national overthrew Queen Liliuokalani, her cabinet, and her marshal, and took over the government of the Kingdom of Hawaii. This led to the 1898 annexation of Hawaii as a United States territory. On August 21, 1959, Hawaii became the 50th state of the United States.
In 1993, one hundred years after the Hawaiian monarchy was overthrown, the United States Congress passed and President Bill Clinton signed the Apology Resolution which “acknowledges that the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and further acknowledges that the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the Kingdom of Hawaii or through a plebiscite or referendum”. As a result, the Hawaiian sovereignty movement, a grassroots political and cultural campaign to reestablish an autonomous or independent nation or kingdom in Hawaii, was established along with ongoing efforts to redress the indigenous Hawaiian population.
********************

Kapiʻolani, Queen Consort of the Hawaiian Islands; Credit – Wikipedia
Kapiʻolani, Queen Consort of the Hawaiian Islands, was the wife of Kalākaua, King of the Hawaiian Islands, who reigned from 1874 to 1891. Kapiʻolani Napelakapuokakaʻe was born on December 31, 1834, in Hilo on the island of Hawaii, then in the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands, now in the state of Hawaii. She was the eldest of the three daughters of High Chief Kūhiō Kalanianaʻole of Hilo and High Chiefess Kinoiki Kekaulike of Kauaʻi, the daughter of King Kaumualiʻi, the last king of an independent Kauaʻi. Kapiʻolani’s Christian name was Esther, but unlike other Christian Hawaiian royals, she and her two sisters never used their Christian names. When Kapiʻolani was sixteen, she was sent to the royal court in Honolulu on the island of Oahu and was under the guardianship of King Kamehameha III. Kapiʻolani learned to understand a few English words and phrases, but she never learned to speak English fluently and required a Hawaiian translator when communicating with English speakers.
Kapiʻolani had two younger sisters:
- Virginia Kapoʻoloku Poʻomaikelani (1839 – 1895), married Hiram Kahanawai, no children
- Victoria Kūhiō Kinoiki Kekaulike (1843 – 1884), married David Kahalepouli Piʻikoi, had three sons
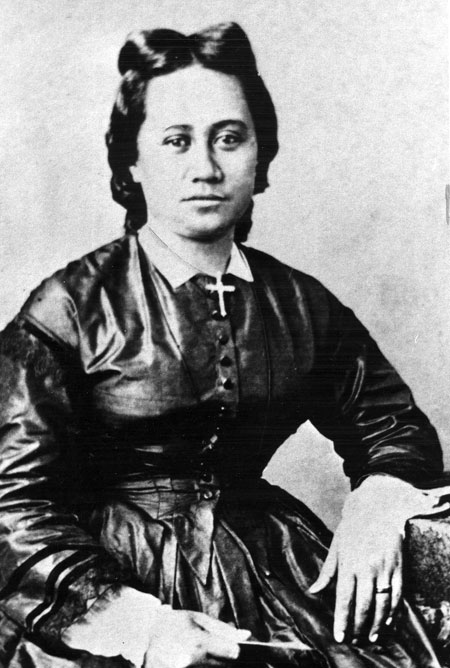
Kapiʻolani in 1852, the year she married Bennett Nāmākēhā; Credit – Wikipedia
On March 7, 1852, 17-year-old Kapiʻolani married 53-year-old High Chief Bennett Nāmākēhā, as his third wife. Bennett was a member of the House of Nobles and the uncle of Queen Emma, the wife of King Kamehameha IV. The marriage was childless, but Kapiʻolani and Bennett were appointed the caretakers of Prince Albert Edward Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa a Kamehameha, the only child of Emma and King Kamehameha IV and Queen Emma. Kapiʻolani also served as a lady-in-waiting to Queen Emma. Sadly, the young prince died in 1862, when he was four years old. Two years earlier, Kapiʻolani’s husband Bennett died on December 27, 1860, aged sixty-one.

David Laʻamea Kamanakapuʻu Māhinulani Nālaʻiaʻehuokalani Lumialani Kalākaua, (King Kalākaua); Credit – Wikipedia
On December 19, 1863, Kapiʻolani married David Laʻamea Kamanakapuʻu Māhinulani Nālaʻiaʻehuokalani Lumialani Kalākaua, the future King Kalākaua, who was only two years older than Kapiʻolani. Their marriage was childless. David’s family was aliʻi nui, Hawaiian nobility, and was distantly related to the reigning House of Kamehameha, sharing common descent from Keaweʻīkekahialiʻiokamoku, King of the island of Hawaii and the great-grandfather of Kamehameha I, the first King of the Kingdom of Hawaii. David’s father Caesar Kapaʻakea was a Hawaiian chief who served in the House of Nobles from 1845 until he died in 1866 and on the King’s Privy Council from 1846 to 1866. David’s mother, Analea Keohokālole, who was of a higher rank than her husband, was a Hawaiian chiefess and a member of the House of Nobles from 1841 to 1847, and on the King’s Privy Council from 1846 to 1847. David was declared eligible to be in the line of succession by the royal decree of King Kamehameha III. He served in the House of Nobles, and the Privy Council of State and held many other court and government posts during the reigns of King Kamehameha IV, King Kamehameha V, and King Lunalilo.
On February 3, 1874, Lunalilo, King of the Hawaiian Islands (born William Charles Lunalilo) died from tuberculosis without naming an heir. As King Lunalilo had wanted to make Hawaii more democratic, it is thought that he wished to have the people choose their next ruler. The Legislature of the Hawaiian Kingdom, the people’s representatives, would choose the next monarch from the eligible royal family members. Queen Emma, the widow of King Kamehameha IV, claimed that King Lunalilo had wanted her to succeed him, but he died before a formal proclamation could be made. She decided to run in the election against David, who had lost to King Lunalilo in a similar election in 1873. While the Hawaiian people supported Emma, it was the legislature that elected the new monarch. They favored David, who won the election 39 – 6. David reigned as King Kalākaua and became the first of two monarchs of the Kingdom of Hawaiian Islands from the House of Kalākaua, who were also the last two monarchs of the Kingdom of Hawaii.
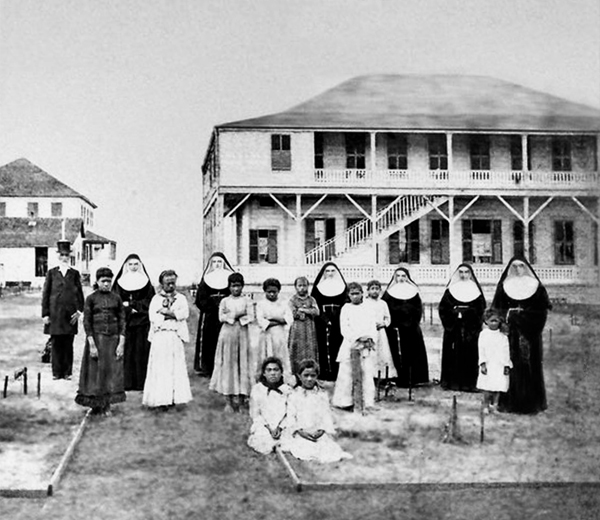

The Sisters of St. Francis and some of the residents of the home Kapiʻolani had built for the children of couples with leprosy; Credit – Wikipedia
As Queen, Kapiʻolani worked to improve the health of the Hawaiian people. She founded the Kapiʻolani Maternity Home in Honolulu, where Hawaiian mothers and their newborn babies could receive care. The Kapiʻolani Maternity Home is still in existence as the Kapiʻolani Medical Center for Women and Children, part of Hawaii Pacific Health’s network of hospitals. Kapiʻolani frequently visited Kakaʻako Branch Hospital on Oʻahu, which served as a receiving station for leprosy patients from all over the islands, and befriended the Roman Catholic Sisters of Saint Francis who staffed the hospital. On July 21, 1884, Kapiʻolani, along with her sister-in-law and her husband Princess Liliuokalani and John Owen Dominis, visited the Kalaupapa Leper Settlement on Molokaʻi where the now famous Belgian priest Father Damien (now Saint Damien of Molokai) spent sixteen years caring for the physical, spiritual, and emotional needs of those in the leper colony before he contracted leprosy. One of the concerns brought to the attention of Queen Kapiʻolani was the welfare of non-leprous children living on the island born to couples with leprosy. Kapiʻolani promised to build a home for these children. After the royal visit, the patients’ living conditions improved significantly.

Princess Liliuokalani (left) and Queen Kapiʻolani (right) at the Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria; Credit – Wikipedia
In April 1887, Queen Kapiʻolani, along with her sister-in-law Princess Liliuokalani and her husband John Owen Dominis, were part of the delegation from the Kingdom of the Hawaiian Islands sent to attend the Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria in London. Kapiʻolani and Liliuokalani were granted an audience with Queen Victoria at Buckingham Palace. They attended the special Jubilee service at Westminster Abbey and were seated with other foreign royal guests.

Queen Kapiʻolani kneeling at the coffin of her husband David (King Kalākaua); Credit – Wikipedia
On November 25, 1890, Kapiʻolani’s husband David set sail for California aboard the USS Charleston. The purpose of the trip was uncertain, but there were reports that the trip was for his ill health. David arrived in San Francisco, California, on December 5, 1890. He suffered a minor stroke in Santa Barbara, California, and was rushed back to San Francisco. Two days before his death, he lapsed into a coma. Kalākaua, King of the Hawaiian Islands, born David Laʻamea Kamanakapuʻu Māhinulani Nālaʻiaʻehuokalani Lumialani Kalākaua died in San Francisco, California, on January 20, 1891, aged 54. He had been under the care of US Navy doctors who listed the cause of his death as nephritis, an inflammation of the kidneys.
After the death of her husband and the accession of her sister-in-law Liliuokalani to the throne, Kapiʻolani retired from public life and rarely attended formal social events. Queen Liliuokalani ruled for two years before she was overthrown. In 1893, a group of local businessmen and politicians, composed of six non-native Hawaiian Kingdom subjects, five American nationals, one British national, and one German national, overthrew Queen Liliuokalani, her cabinet, and her marshal, and took over the government of the Kingdom of Hawaii. This led to the 1898 annexation of Hawaii as a United States territory.

Tomb of Queen Kapiʻolani and her husband David (King Kalākaua); Credit – Wikipedia
Kapiʻolani lived out the remainder of her life at her private residence, Pualeilani, in Waikīkī, Honolulu, on the island of Oahu, where the Hyatt Regency Waikiki now stands. During the last two years of her life, Kapiʻolani suffered three strokes. She died, aged sixty-four, at her home on June 24, 1899. After a funeral at the Kawaiahaʻo Church in Honolulu officiated by the Anglican Bishop Alfred Willis, Kapiʻolani was buried in the Royal Mausoleum at Mauna ʻAla. Due to overcrowding, in 1907, the Territory of Hawaii allocated $20,000 for the construction of a separate underground vault for the Kalākaua family. Kapiʻolani’s coffin and the coffins of the Kalākaua family were transferred to the new underground Kalākaua Crypt in a ceremony on June 24, 1910, officiated by her sister-in-law, the former Queen Liliuokalani.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- Flantzer, Susan. (2024). Kalākaua, King of the Hawaiian Islands. Unofficial Royalty. https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/kalakaua-king-of-the-hawaiian-islands/
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Hawaiian Kingdom. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hawaiian_Kingdom
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024). Kalākaua. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kal%C4%81kaua
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2024a, January 6). Kapiʻolani. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kapi%CA%BBolani
- Wikimedia Foundation. (2023). Royal Mausoleum (Mauna ʻAla). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Mausoleum_(Mauna_%CA%BBAla)
