by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2021
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was located in today’s southern Italy. It included the island of Sicily and all of the Italian peninsula south of the Papal States. Ferdinando I, the first King of the Two Sicilies, had previously reigned over two kingdoms, as Ferdinando IV of the Kingdom of Naples and Ferdinando III of the Kingdom of Sicily. He had been deposed twice from the throne of Naples: once by the revolutionary Parthenopean Republic for six months in 1799 and again by Napoleon in 1805, before being restored in 1816 after the defeat of Napoleon. After the 1816 restoration, the two kingdoms were united into the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
Vittorio Emanuele II, King of Sardinia became a driving force behind the Italian unification movement along with Giuseppe Garibaldi, a general and nationalist, and Giuseppe Mazzini, a politician and journalist. Garibaldi conquered Naples and Sicily, the territories of the Kingdom of Two Sicilies. Francesco II, King of the Two Sicilies was deposed, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ceased to exist, and its territory was incorporated into the Kingdom of Sardinia. Eventually, the Sardinian troops occupied the central territories of the Italian peninsula, except Rome and part of Papal States. With all the newly acquired land, Vittorio Emanuele II was proclaimed the first King of the new, united Kingdom of Italy in 1861.
********************

Francesco I, King of the Two Sicilies; Credit – Wikipedia
King of the Two Sicilies for only five years, Francesco Gennaro Giuseppe Saverio Giovanni Battista was born in the Royal Palace of Naples in the Kingdom of Naples, now in Italy, on August 19, 1777. He was the fifth of the seventeen children and the second but the eldest surviving of the seven sons of Ferdinando, who reigned as King of Naples and King of Sicily from 1759 – 1816, and then as King Ferdinando I of the Two Sicilies from 1816 – 1825, and his first wife Archduchess Maria Carolina of Austria. Francesco’s paternal grandparents were Carlos III, King of Spain and Maria Amalia of Saxony. His maternal grandparents were the formidable and powerful Holy Roman Empress Maria Theresa, who was in her own right Archduchess of Austria, Queen of Hungary, Queen of Croatia, and Queen of Bohemia, and Franz, Holy Roman Emperor, Grand Duke of Tuscany, and Duke of Lorraine. Even though her husband was the nominal Holy Roman Emperor, Maria Theresa wielded the real power.

Included in the portrait are Ferdinando, Maria Carolina, and their children Maria Theresa, Maria Luisa, Maria Amelia, Francesco, Maria Cristina, and Gennaro, 1783; Credit – Wikipedia
Upon the death of his three-year-old elder brother Carlo, Duke of Calabria from smallpox, Francesco became the heir-apparent to the thrones of Naples and Sicily and Duke of Calabria, the traditional title of the heir apparent to the throne of Naples. Six more of Francesco’s sixteen siblings would also die from smallpox.
- Maria Teresa of Naples and Sicily (1772 – 1807), married her first cousin Franz II, Holy Roman Emperor (later Franz I, Emperor of Austria), had twelve children, died in childbirth
- Luisa of Naples and Sicily (1773 – 1802), married her first cousin Ferdinand III, Grand Duke of Tuscany, had five children, died in childbirth
- Carlo of Naples and Sicily, Duke of Calabria (1775 – 1778), died in early childhood from smallpox.
- Maria Anna of Naples and Sicily (1775 – 1780), died in childhood from smallpox.
- Maria Cristina of Naples and Sicily (1779 – 1849), married Carlo Felice, King of Sardinia, no children
- Gennaro of Naples and Sicily (1780 – 1789), died in childhood from smallpox
- Giuseppe of Naples and Sicily (1781 – 1783), died in early childhood from smallpox.
- Maria Amelia of Naples and Sicily (1782 – 1866), married Louis Philippe d’Orléans, Duke of Orléans, later King of the French, had ten children
- Maria Carolina of Naples and Sicily (born and died 1783)
- Maria Antonia of Naples and Sicily (1784 – 1806), married Infante Ferdinand of Spain, Prince of Asturias, later King Ferdinand VII of Spain, no children, died from tuberculosis
- Maria Clotilde of Naples and Sicily (1786 – 1792), died in childhood from smallpox
- Maria Enricheta of Naples and Sicily (1787- 1792), died in childhood from smallpox
- Carlo Gennaro of Naples and Sicily (1788 – 1789), died in infancy from smallpox
- Leopoldo of Naples and Sicily (1790 – 1851), married his niece Clementina of Austria, had two children
- Alberto of Naples and Sicily (1792 – 1798), died in childhood
- Maria Isabella of Naples and Sicily (1793 – 1801), died in childhood
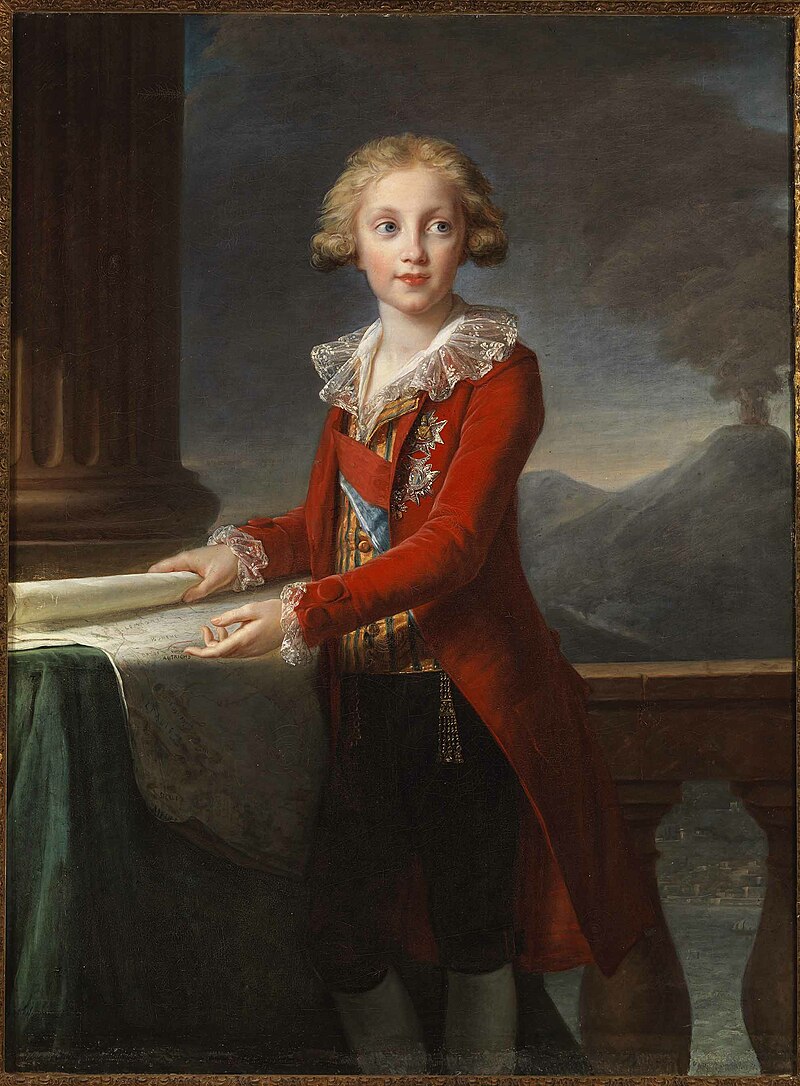

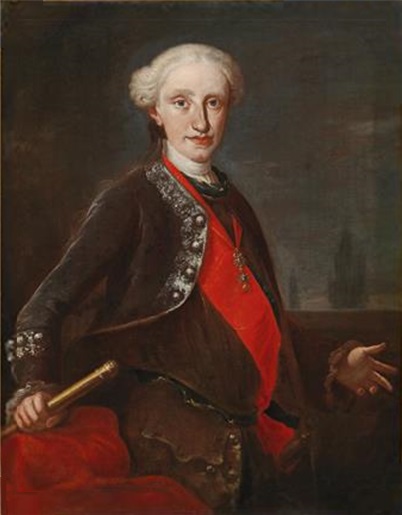
Francesco at the age of thirteen; Credit – Wikipedia
Unlike his father who received no comprehensive education, Francesco was well educated by highly qualified tutors such as physicist and biologist Giuseppe Saverio Poli and Cardinal Domenico Orsini d’Aragona. He showed great interest in history and the natural sciences, particularly botany. When Francesco was eighteen years old, he began to attend meetings of the state council so that he could learn about the government.

Francesco’s mother Maria Carolina of Austria; Credit – Wikipedia
Francesco’s mother Maria Carolina of Austria had been extremely well educated and prepared for her role as Queen Consort. As part of her marriage contract, Maria Carolina was to have a place on the council of state after the birth of her first son. In 1775, after her first son was born, Maria Carolina took her place on the council of state. Bernardo Tanucci, the former president of her husband’s regency council, was still on the council of state and attempted to thwart her political influence, and found himself dismissed in 1777. From then on, Maria Carolina was the de facto ruler of the Kingdoms of Naples and Sicily.

Maria Clementina of Austria, Francesco’s first wife; Credit – Wikipedia
Francesco accepted his mother’s plan that he marry his double first cousin Archduchess Maria Clementina of Austria, the daughter of Leopold II, Holy Roman Emperor and Maria Luisa of Spain. Leopold II was the brother of Francesco’s mother and Maria Luisa was the sister of Francesco’s father. The marriage was planned to strengthen the alliance between Naples and Sicily and Austria. A proxy marriage took place in 1790. However, because the bride and the groom were both only thirteen years old and the French Revolution caused unrest in Europe, the actual wedding did not occur for seven years. On June 25, 1797, Francesco and Maria Clementina were married in person in Foggia, Kingdom of Naples, now in Italy.
Francesco and Maria Clementina had two children:
- Maria Carolina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1798 – 1870), married (1) Charles Ferdinand d’Artois, Duke of Berry, had two surviving children (2) Ettore Carlo Lucchesi-Palli, 8th Duke della Grazia, had five children
- Fernando Francesco of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1800 – 1801), died in infancy

Maria Isabella of Spain, Francesco’s second wife; Credit – Wikipedia
Maria Clementina died from tuberculosis in Naples, Kingdom of Naples on November 15, 1801, aged 24, and was buried at the Basilica of Santa Chiara, Naples. After her death, a double marriage was arranged with Spain. Carlos IV, King of Spain was the brother of Ferdinando I, King of Naples and Sicily, and so these marriages were between first cousins. Francesco was to marry Maria Isabella of Spain and his sister Maria Antonia was to marry Ferdinand of Spain, Prince of Asturias, later King Ferdinand VII of Spain. Maria Antonia died in 1806 from tuberculosis before her husband became King of Spain. On July 6, 1802, in Madrid Spain, 13-year-old Maria Isabella married her 25-year-old cousin Francesco by proxy with her brother Ferdinand standing in for the groom. The two couples were married in person in Barcelona, Spain on October 4, 1802.

Francesco’s family: Left to right: Maria Isabella, second wife of Francesco holding Maria Carolina, Ferdinanda Luisa, Maria Antonia, Luisa Carlotta, Maria Cristina, Ferdinando, Francesco holding Maria Amalia, Carlo, Prince of Capua and Leopoldo, Count of Syracuse; Credit – Wikipedia
Francesco and Maria Isabella had twelve children over twenty-three years. Unusual for the time, all twelve survived childhood.
- Luisa Carlotta of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1804 – 1844), married her maternal uncle Francisco de Paula of Spain, had eleven children
- Maria Cristina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1806 – 1878), married (1) her maternal uncle Ferdinand VII, King of Spain, had two daughters including Queen Isabella II of Spain (2) Agustín Fernando Muñoz y Sánchez, 1st Duke of Riánsares, had eight children
- Ferdinando II, King of the Two Sicilies (1810 – 1859), married (1) Maria Cristina of Savoy, had one child Francesco II, King of the Two Sicilies, died from childbirth complications (2) Maria Theresa of Austria, had twelve children
- Carlo Ferdinando of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Prince of Capua (1811 – 1862), married morganatically Penelope Smyth, had two children
- Leopoldo Beniamino of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Count of Syracuse (1813 – 1860), Maria of Savoy-Carignan, had one daughter who died in infancy
- Maria Antonia of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1814 – 1898), married Leopold II, Grand Duke of Tuscany, had ten children
- Antonio Pasquale of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Count of Lecce (1816 – 1843), unmarried, clubbed to death by the husband of a married woman he had tried to seduce
- Maria Amalia of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1818 – 1857), married Infante Sebastian of Portugal and Spain, no children
- Maria Carolina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1820 – 1861), married Carlos of Spain, Count of Montemolin, Carlist pretender to the Spanish throne, no children
- Teresa Cristina of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (1822 – 1889), married Emperor Pedro II of Brazil, had four children
- Luigi Carlo of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Count of Aquila (1824 – 1897), married Januária, Princess Imperial of Brazil, had four children
- Francesco di Paola of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, Count of Trapani (1827 – 1892), married his niece Maria Isabella of Austria, Princess of Tuscany, had six children
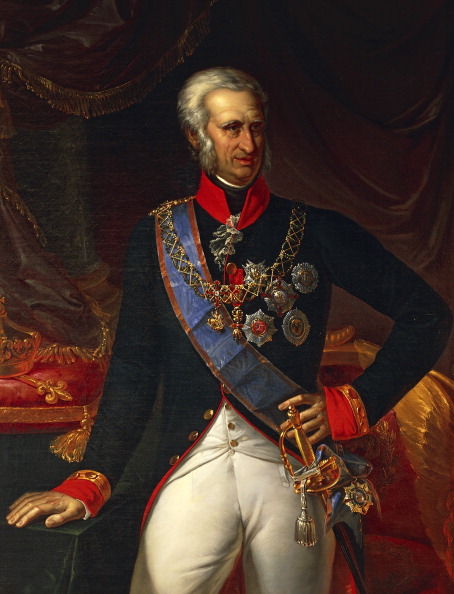

Francesco’s father Ferdinando I, King of the Two Sicilies; Credit – Wikipedia
Francesco’s father Ferdinando was deposed twice from his thrones: once by the revolutionary Parthenopean Republic for six months in 1799 and again by Napoleon in 1805. In February 1806, Ferdinando, Maria Carolina, and their family were forced to flee to the island of Sicily, which was still in their control, where they lived in the Royal Palace of Palermo under British protection. However, the government of Sicily was a feudal type, and the British insisted on a government more similar to the British one. In 1813, Ferdinando essentially but not officially abdicated and Francesco was appointed regent. At the insistence of the British, who were becoming more and more adverse to Maria Carolina, she was forced to leave Sicily. She returned to her home in Austria where she died from a stroke, aged 62, on September 8, 1814.
Less than three months after the death of his mother Maria Carolina, Francesco’s father Ferdinand married again to Lucia Migliaccio, Duchess of Floridia. The marriage caused a considerable scandal. Francesco had tried to dissuade his father from marrying Lucia, and always intensely disliked her. In 1816, after Ferdinando abolished the constitution of the Kingdom of Sicily, the two kingdoms, Naples and Sicily, were united into the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. For the next four years, Ferdinand reigned as an absolute monarch, and there were no constitutional reforms. In 1820, a revolt broke out in Sicily and riots occurred in Naples. Ferdinando was forced to sign a constitution and appoint his son Francesco as regent of Sicily. This only lasted until March 1821, when Austrian troops friendly to Ferdinando occupied Naples. Ferdinando was re-established as an absolute monarch and the constitution was withdrawn. Ferdinando died from a stroke on January 4, 1825, at the age of 73 and his son Francesco became King of the Two Sicilies.
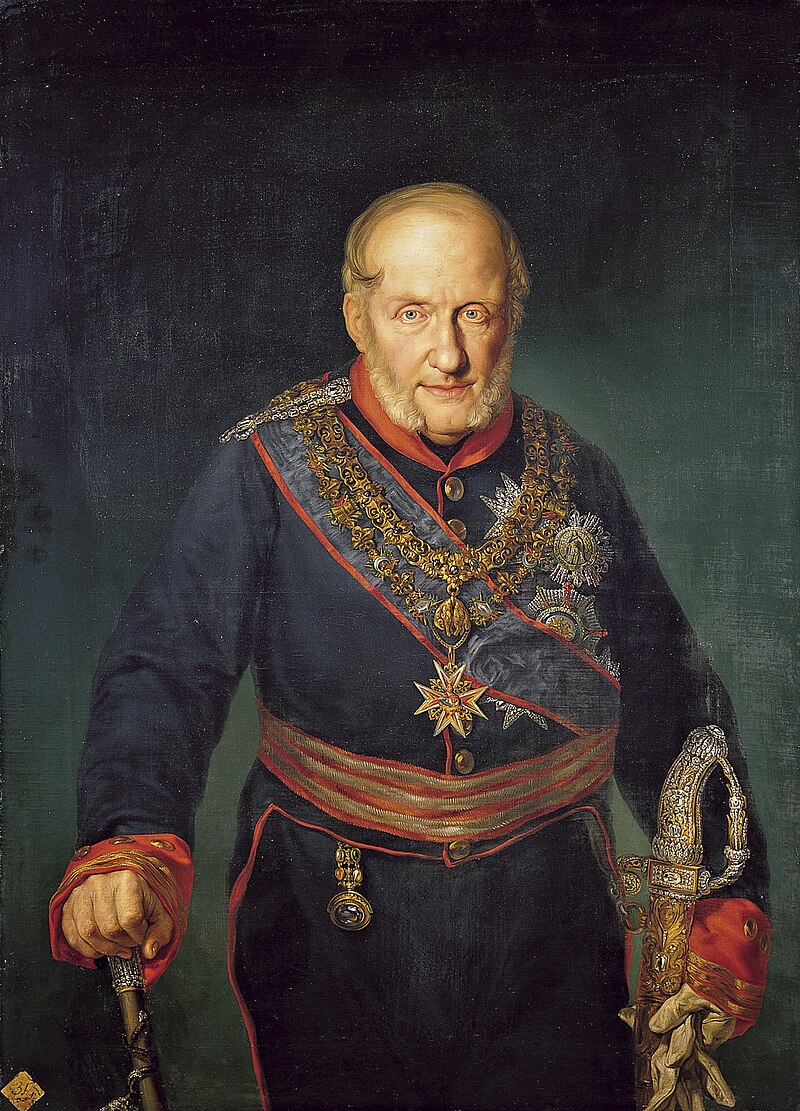

Francesco I, King of the Two Sicilies, 1829; Credit – Wikipedia
After his father’s death, Francesco expelled his stepmother Lucia Migliaccio, Duchess of Floridia from the royal court. When Lucia died in 1826, noticeably missing from her funeral were Francesco and members of the royal family of the Two Sicilies. Francesco wanted to demonstrate once and for all the true feelings he had for Lucia. As king, Francesco followed conservative policies. He was content to leave the government in the hands of his favorites and advisers. During Francesco’s reign, the Carbonari, an informal network of secret revolutionary societies, grew stronger especially in eastern Sicily and in the Italian mainland part of the kingdom. In Sicily, smuggling and corruption flourished. Numerous crimes were committed by private armed gangs in the service of nobles and large landowners, from which the Cosa Nostra, also known as the Sicilian Mafia, later developed. Francesco’s major success was having the Austrian occupation force withdrawn, relieving a large financial burden on the treasury.

Coat of arms of the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies on the entrance to the royal crypt; Credit – Di Giuseppe Guida – Flickr: Basilica di Santa Chiara., CC BY 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=20267754
Francesco I, King of the Two Sicilies died on November 8, 1830, aged 53, in Naples, Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, now in Italy. He was buried at the Basilica of Santa Chiara in Naples, the traditional burial site of the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies. His second wife Maria Isabella survived him by eighteen years, dying on September 13, 1848, at the age of 59, at the Palace of Portici in Portici, Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, now in Italy. She was buried with her husband at the Basilica di Santa Chiara.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies Resources at Unofficial Royalty
Works Cited:
- De.wikipedia.org. 2021. Franz I. (Sizilien) – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Franz_I._(Sizilien)> [Accessed 6 August 2021].
- En.wikipedia.org. 2021. Francis I of the Two Sicilies – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Francis_I_of_the_Two_Sicilies> [Accessed 6 August 2021].
- Flantzer, Susan, 2021. Ferdinando I, King of the Two Sicilies. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/ferdinando-i-king-of-the-two-sicilies/> [Accessed 6 August 2021].
- It.wikipedia.org. 2021. Francesco I delle Due Sicilie – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Francesco_I_delle_Due_Sicilie> [Accessed 6 August 2021].