by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2019

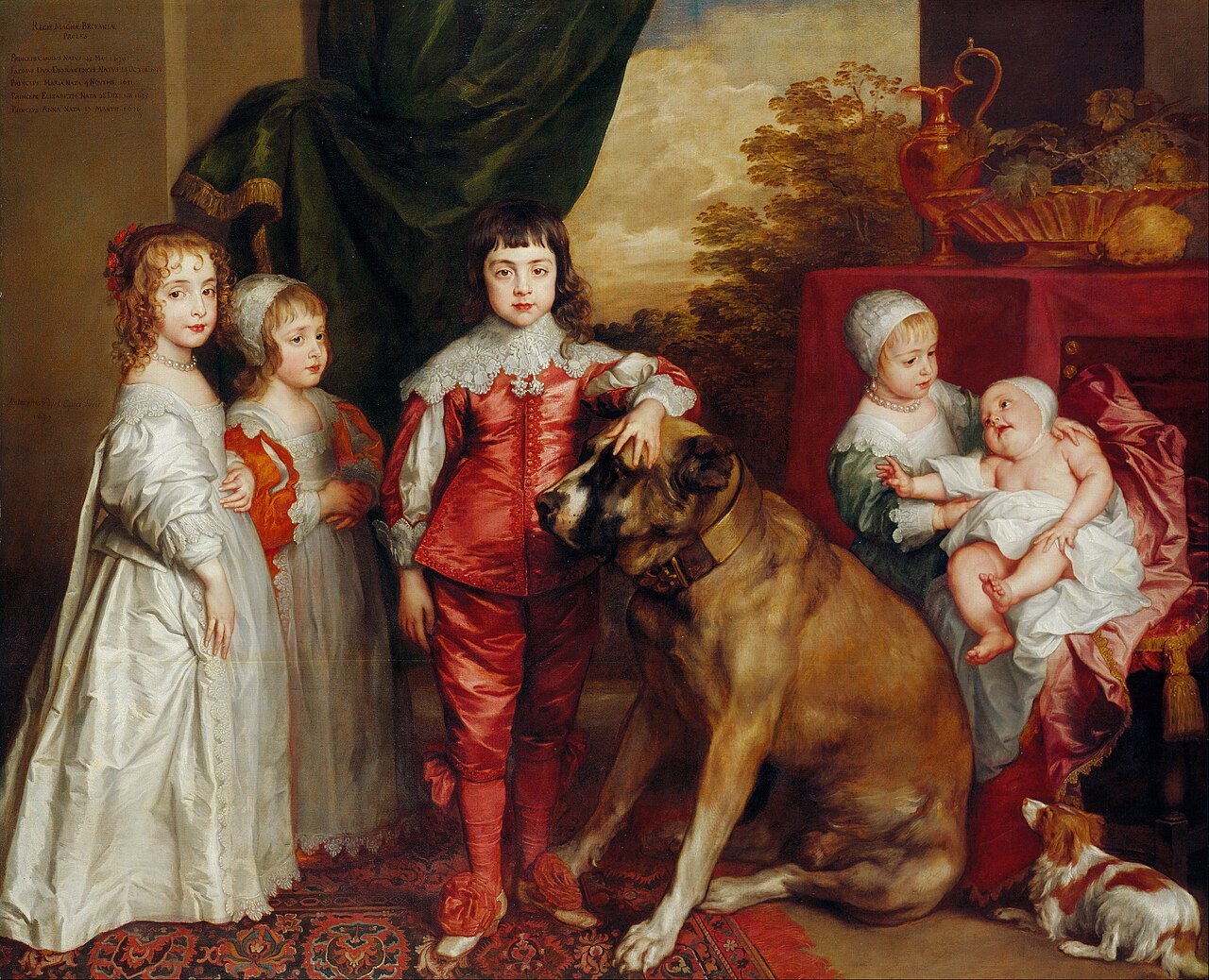
Charles I, King of England, King of Scots (1600 – 1649)
(All photos credits – Wikipedia unless otherwise noted)
Charles I was born at Dunfermline Palace in Fife, Scotland while his father was only King of Scots. He was the second son and fourth of the seven children of James VI, King of Scots (later also King James I of England) and Anne of Denmark. Charles’ paternal grandparents were Mary, Queen of Scots and Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley, who were both grandchildren of Margaret Tudor, elder sister of King Henry VIII of England. His maternal grandparents were King Frederik II of Denmark and Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow. When Queen Elizabeth I of England died, Charles’ father also became King James I of England. Since none of the children of King Henry VIII of England had children, James was the senior heir of King Henry VII of England through his eldest daughter Margaret Tudor. The family then moved to England.
Charles was not expected to be king as he had an elder brother Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales who was named after his grandfathers. When 18-year-old Henry died from typhoid fever, Charles became heir to the thrones of England and Scotland. He married Henrietta Maria, the youngest child of King Henri IV of France and his second wife, Marie de’ Medici. They had nine children including King Charles II and King James II.
Charles had issues with Parliament, clashing with its members over financial, political and religious issues. The situation got worse when Charles committed the unprecedented act of entering the House of Commons with an armed guard and demanding the arrest of five Members of Parliament. There was a great public outcry, Charles fled London and civil war appeared inevitable. The English Civil War led to Charles being tried and convicted for treason and other high crimes. He was beheaded at the Palace of Whitehall in London where a scaffold had been built outside the Banqueting House.
King Charles I shared his first cousins with his siblings Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales; Elizabeth Stuart, Electress Palatine of the Rhine; Margaret Stuart; Robert, Duke of Kintyre; Mary Stuart; and Sophia Stuart. Charles I had no paternal aunts and uncles because his father King James I was an only child. Therefore, Charles I had no paternal first cousins.
********************
Maternal Aunts and Uncles: Children of King Frederik II of Denmark and Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow
- Elisabeth of Denmark, Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1573 – 1626), married Heinrich Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, had five sons and five daughters
- King Christian IV of Denmark and Norway (1577 – 1648), married (1) Anne Catherine of Brandenburg, had four sons and two daughters (2) morganatically Kirsten Munk, had eight daughters and two sons
- Ulrik of Denmark, Prince-Bishop of Schwerin (1578 – 1624), morganatically married Katarina Hahn-Hinrichshagen
- Hans August of Denmark (born and died 1579), died in infancy
- Augusta of Denmark, Duchess of Holstein-Gottorp (1580 – 1639), married Johann Adolf, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp, had four sons and four daughters
- Hedwig of Denmark, Electress of Saxony (1581 – 1641), married Christian II, Elector of Saxony, no children
- Hans of Denmark (1583 – 1602), unmarried
********************
MATERNAL FIRST COUSINS
Maternal First Cousins: Children of Elisabeth of Denmark, Duchess of Brunswick-Lüneburg and Heinrich Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Prince of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel

Friedrich Ulrich, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1591 – 1634)
Because of his alcoholism, Friedrich Ulrich was temporarily deposed by his mother with the help of her brother King Christian IV of Denmark. Eventually, he was allowed to regain control but his ineffective rule caused the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg to lose much territory during the Thirty Years’ War. Friedrich Ulrich married Anna Sophia of Brandenburg but their marriage was unhappy and they had no children.
********************

Sophia Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Countess of Nassau-Dietz (1592 – 1642)
Sophia Hedwig married Ernst Casimir I, Count of Nassau-Dietz and had four sons and two daughters but only two sons survived childhood. After the death of her husband, Sophia Hedwig was instrumental in limiting the damage to the County of Nassau-Dietz during the Thirty Years’ War.
********************

Elisabeth of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Duchess of Saxe-Altenburg (1593 – 1650)
When Elisabeth was 19-years-old, she married August, Duke of Saxony. The couple had no children and August died suddenly after three years of marriage. She made a second marriage to Johann Philip, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg and had one daughter. Through their daughter Elisabeth Sophie who married Ernst I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha, Elisabeth and Johann Philip are the ancestors of Queen Victoria and her husband Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha.
********************

Hedwig of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Duchess of Pomerania (1595 – 1650)
Hedwig married Ulrich, Duke of Pomerania but the marriage was childless. Ulrich died three years after the marriage. Hedwig never remarried. She wore mourning clothes for the rest of her life and devoted herself to charity.
********************

Dorothea of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Margravine of Brandenburg (1596 – 1643)
Dorothea was the first of the three wives of Christian Wilhelm, Margrave of Brandenburg. The couple had one daughter. During their marriage, Dorothea’s husband converted to Roman Catholicism and he tried to influence their daughter Sophie Elisabeth to also convert. Dorothea sent her daughter to live with her sister Hedwig to prevent the conversion.
********************
Heinrich Julius of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1597 – 1606), died in childhood
********************

Christian the Younger of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1599 – 1626)
Christian was titular Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Halberstadt, and a German Protestant military leader during the early years of the Thirty Years’ War. He never married and died on battle wounds at the age of 26.
********************

Rudolf’s tomb; Credit – Von Mogadir – Eigenes Werk, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=29388237
Rudolf of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1602 – 1616)
Rudolf died two days before his 14th birthday while studying at the University of Tübingen, now in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, and was buried in the Tübingen Collegiate Church.
- Wikipedia: Rudolf of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (in German)
********************
Heinrich Karl of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1609 – 1615), died in childhood
********************
Anna Augusta of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Countess of Nassau-Dillenburg (1612 – 1673)
Anna married Georg Ludwig, Count of Nassau-Dillenburg, who was the Hereditary Prince of Nassau-Dillenburg. He never became Prince of Nassau-Dillenburg because he predeceased his father. Anna and Georg Ludwig had five daughters and one son.
********************
Maternal First Cousins: Children of King Christian IV of Denmark and Norway and his first wife Anne Catherine of Brandenburg
Frederik of Denmark (born and died 1599), died in infancy
********************

Christian, Prince-Elect of Denmark (1603 – 1647)
Christian was appointed by the Royal Council as heir to the throne of Denmark. He was a great collector of antiques and works of art. He married Magdalene Sibylle of Saxony, daughter of the Johann Georg I, Elector of Saxony, but the couple had no children. As a result of his unhealthy lifestyle, Christian predeceased his father.
********************
Sophie of Denmark (born and died 1605), died in infancy
********************
Elisabeth of Denmark (1606 – 1608), died in childhood
********************

Frederik III, King of Denmark and Norway (1609 – 1670)
During his childhood and early adulthood, Frederik had no prospect of becoming. However, when he was 38-years-old, his elder brother Christian died and Frederik was elected heir by the Royal Council. During Frederik’s reign, an absolute monarchy was established which lasted almost 150 years in Norway and over 200 years in Denmark. Frederik married Sophie Amalie of Brunswick-Lüneburg and had three sons and five daughters including George who married Queen Anne of Great Britain.
********************
Ulrik of Denmark, Prince-Bishop of Schwerin (1611 – 1633)
When Ulrik was 13-years-old, he was appointed administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Schwerin. During the Thirty Years’ War, fought between various Protestant and Catholic states in the Holy Roman Empire, Ulrik served in the army of the Electorate of Saxony. After a dinner with imperial officers during a truce, Ulrik was fatally wounded by an unexpected shot fired an imperial knight and died the next evening.
********************
Maternal First Cousins: Children of King Christian IV of Denmark and Norway and his morganatic second wife Kirsten Munk
Christian IV’s morganatic wife and their children were given the title Count or Countess of Schleswig-Holstein.
Countess Anna Catharine of Schleswig-Holstein (1618 – 1633)
Anna Catharine married Frands Rantzau, who had become a member of the Danish Council of State and a state governor in Copenhagen at the age of only 22. Frands drowned in the moat at Rosenborg Castle in Copenhagen after a party with Anna Catharine’s father. The following year, 15-year-old Anna Catharine died.
********************
Countess Sophie Elisabeth of Schleswig-Holstein (1619 – 1657)
Sophie Elisabeth married Christian von Pentz, Governor of Glückstadt and a diplomat in the service of King Christian IV.
********************

Countess Leonora Christina of Schleswig-Holstein (1621 – 1698)
Leonora Christina married Corfitz Ulfeldt, a Danish nobleman and statesman who is considered the worst traitor in Danish history. The couple had seven sons and three daughters and through their youngest child Austrian Field Marshal Count Leo Ulfeldt, they are the ancestors of many noble and royal families. Their descendants include Tsar Simeon II of Bulgaria, King Michael of Romania, Prince Hans Adam II of Liechtenstein, Emperor Karl I of Austria-Hungary, King Peter II of Yugoslavia, King Manuel II of Portugal, and Marie Christine, Princess Michael of Kent.
Leonora Christina’s husband was rumored to have been associated with a plot to poison her half-brother King Frederik III and his family. They both left Denmark and for several years and traveled around Europe avoiding capture. Ulfeldt offered Elector Friedrich Wilhelm, Elector of Brandenburg to incite a revolt in Denmark in order to put him on the Danish throne. The Elector himself communicated this treason to King Frederik III and Ulfeldt was tried for treason in absentia and condemned to be beheaded and quartered. Instead of submitting himself to execution, Ulfeldt apparently drowned himself in the Rhine River near Basel, Switzerland.
Leonora Christina was eventually captured and was imprisoned for 22 years in the Blue Tower of Christiansborg Palace in Copenhagen. She was not released until the death of Queen Dowager Sophie Amalie, the widow of King Frederik III, Leonora Christina’s half-brother. While imprisoned, Leonora Christina wrote her memoirs Jammers Minde (A Memory of Lament), considered to be Denmark’s most important 17th-century prose work.
********************

Count Valdemar Christian of Schleswig-Holstein (1622 – 1656)
Valdemar Christian was sent to Russia to marry Irina Mikhailovna, the eldest daughter of Michael, Tsar of All Russia. After arriving in Russia, Valdemar refused to convert to the Russian Orthodox religion. Valdemar was imprisoned for a year and then was finally allowed to leave Russia. He had issues with his half-brother King Frederik III because Valdemar wanted to be elected king instead of Frederik. Because of the dispute, Valdemar decided to leave Denmark. He served in the Swedish Army and was killed in battle in Poland
********************

Countess Elisabeth Auguste of Schleswig-Holstein (1623 – 1677)
Elisabeth Auguste married Hans Hansen Lindenov, a member of the Council of State and had one daughter. She was considered vulgar and was always in debt because of her gambling habit. Even after being granted a royal pension, her problems with money continued.
********************
Count Friedrich Christian of Schleswig-Holstein (1625 – 1627), died in early childhood
********************
Countess Christiane of Schleswig-Holstein (1626 – 1670)
Christiane was the twin sister of Hedwig. At the age of ten, she was engaged to marry Hannibal Sehested, Governor-General of Norway. The marriage took place when Christiane was 16-years-old and thereafter, she left for Norway with her husband where they lived in Akershus Fortress in Oslo. Christiane and Hannibal had one daughter. Hannibal was accused of embezzlement which resulted in him surrendering all his private property in Norway to the crown. Christiane lost her title of Countess and all her private property. Eventually, they were reconciled with the Danish court and Christiane’s title and property were returned.
********************

Countess Hedwig of Schleswig-Holstein (1626 – 1678)
Hedwig was the twin sister of Christiane. She married Ebbe Ulfeldt, a cousin of the traitor Corfitz Ulfeldt mentioned above. Ebbe was an officer in the Danish Navy and later a landscape painter. Hedwig and Ebbe had one daughter. Their marriage was unhappy and eventually, Hedwig left her husband.
********************
Countess Maria Katharina of Schleswig-Holstein (born and died 1628), died in infancy
********************
Maternal First Cousins: Children of Augusta of Denmark and Duke Johann Adolf of Holstein-Gottorp

Friedrich III, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp (1597 – 1659)
Friedrich married Marie Elisabeth of Saxony and had eight daughters and eight sons. Friedrich and his wife are great-great-grandparents of Catherine II (the Great), Empress of All Russia.
Friedrich had ambitious plans concerning the development of sea trade which were, for the most part, unsuccessful. His alliance with Sweden during the Thirty Years’ War which included marrying his daughter Hedwig Eleonora to King Carl X of Sweden, ultimately weakened the Duchy of Holstein-Gottorp because Sweden failed at establishing itself as a Great Power.
********************
Elisabeth Sofie of Holstein-Gottorp (1599 – 1627)
Elisabeth Sofie was the first wife of Augustus, Duke of Saxe-Lauenburg. They had three daughters and three sons. Elisabeth Sofie died from childbirth complications shortly after the birth of her last child who lived for only five days.
********************

Adolf of Holstein-Gottorp (1600 – 1631)
Adolf fought in the Thirty Years’ War for the Catholic Holy Roman Empire against the forces of his uncle King Christian IV and other Protestant rulers. He was severely wounded at the Battle of Breitenfeld and died two days later.
********************
Dorothea Augusta of Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp (1602 – 1682)
Dorothea Augusta married Joachim Ernest, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Plön. They had five sons and three daughters.
********************
Hedwig of Holstein-Gottorp (1603 – 1657)
Hedwig married Augustus, Count Palatine of Sulzbach and had four sons and three daughters.
********************
Anna of Holstein-Gottorp (1605 – 1623)
********************

Johann of Holstein-Gottorp (1606 – 1655)
Johann was a Lutheran Administrator of Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. He married Julia Felicitas of Württemberg-Weiltingen and had three sons and one daughter. The marriage was very unhappy and the couple eventually divorced.
Wikipedia: Johann of Holstein-Gottorp
********************
Christian of Holstein-Gottorp (born and 1609), died in infancy
********************
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
-
- Lundy, D. (2019). Main Page. [online] Thepeerage.com. Available at: http://www.thepeerage.com/. (for genealogy information)
- Unofficial Royalty. (2019). Unofficial Royalty. [online] Available at: https://www.unofficialroyalty.com. (for biographical and genealogy information)
- Wikipedia. (2019). Main Page. [online] Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/. (for biographical and genealogy information)