by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2022

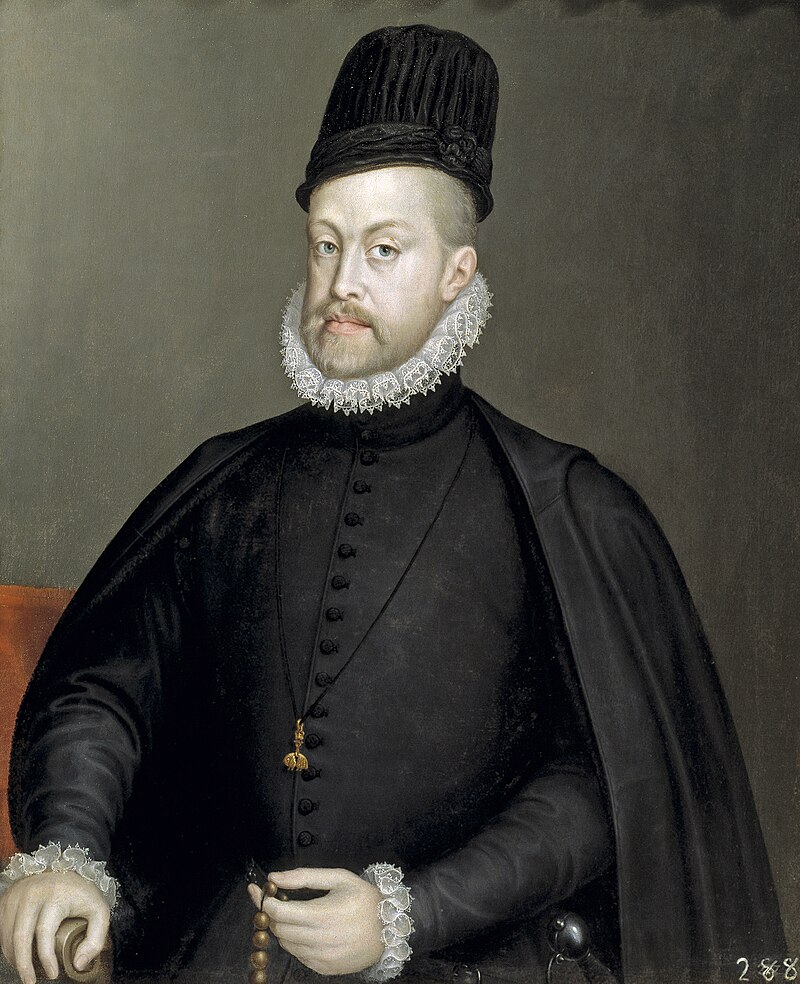
Felipe IV, King of Spain, Filipe III, King of Portugal; Credit – Wikipedia
Besides being King of Spain, Felipe was also King of Portugal (from 1621 to 1640) and King of Sardinia, King of Naples, King of Sicily, Duke of Milan, Duke of Lothier, Duke of Brabant, Duke of Limburg, Duke of Luxemburg, Count Palatine of Burgundy, Count of Flanders, Count of Hainaut and Count of Namur from 1621 until his death in 1665.
Felipe Domingo Víctor de la Cruz was born on April 8, 1605, at the Royal Palace of Valladolid in Valladolid, Spain. He was the eldest of the four sons and third but the second surviving of the eight children of Felipe III, King of Spain and Margaret of Austria. His paternal grandparents were Felipe II, King of Spain and his fourth wife and niece Anna of Austria. Felipe IV’s maternal grandparents were Karl II, Archduke of Austria-Styria and his niece Maria Anna of Bavaria. As the heir to the Spanish throne, Felipe was titled Prince of Asturias.
The House of Habsburg was notorious for its inbreeding. The Habsburgs had built their empire by marriage and they wanted to keep the land they amassed all in the family, so they began to intermarry more and more frequently among themselves. Of the eleven marriages of Spanish monarchs between 1450 and 1661, nearly all contained some element of consanguinity, marriages between very closely related people. Felipe IV’s parents, King Felipe III and Margaret of Austria, both children of parents who were an uncle and his niece, were first cousins once removed and second cousins, adding to more inbreeding.

Felipe with his elder sister Ana María Mauricia: Credit – Wikipedia
Felipe IV had seven siblings but only four survived childhood. His elder sister Ana María Mauricia, better known as Queen Anne of France, married King Louis XIII of France. They were the parents of King Louis XIV of France. When Felipe IV was ten years old, his mother died at the age of twenty-six from childbirth complications eleven days after giving birth to her eighth child.
Felipe IV’s siblings:
- Ana María Mauricia of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1601 – 1666), married Louis XIII, King of France, had two sons Louis XIV, King of France and Philippe I, Duke of Orléans
- Maria of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1603)
- Maria Anna of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1606 – 1646), married Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor, had six children including Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor and Marianna of Austria who married her maternal uncle Felipe IV, King of Spain
- Carlos of Austria, Infante of Spain (1607 – 1632), unmarried
- Ferdinand of Austria, Cardinal-Infante of Spain (1609 – 1641), unmarried
- Margarita of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1610 – 1617), died in childhood
- Alonso of Austria, Infante of Spain (1611 – 1612), died in infancy
An assassination caused an early marriage for Felipe IV. On May 14, 1610, King Henri IV of France was assassinated by a Catholic zealot François Ravaillac, and his nine-year-old son ascended the French throne as King Louis XIII. The widowed Queen, Marie de’ Medici, was appointed Regent for her son. During this period, there were struggles in France between the Catholics and the Protestants (French Huguenots). The new Regent, Marie de’ Medici promoted a strong alliance with the Spanish monarchy and favored Catholicism over Protestantism. To strengthen this bond, she arranged the marriages of her son King Louis XIII to Felipe IV’s elder sister Ana María Mauricia and her eldest daughter Elisabeth of France to the future King Felipe IV of Spain.

Felipe IV’s first wife Elisabeth of France; Credit – Wikipedia
On August 13, 1615, at the Louvre Palace in Paris, France, both young couples were married by proxy and soon, Elisabeth and her brother Louis XIII left Paris to meet their respective spouses. On Pheasant Island in the Bidassoa River that divides France and Spain, the two couples first met and the brides were exchanged. On November 25, 1615, at the Cathedral of St. Mary in Burgos, Spain, 13-year-old Elisabeth married 10-year-old Felipe in a religious ceremony.
Because of the couple’s young age, the marriage was not consummated. The situation changed when Elisabeth’s father-in-law King Felipe III became ill, the marriage was consummated, and Elisabeth quickly became pregnant. King Felipe III died on March 31, 1621, and was succeeded by his 16-year-old son as King Felipe IV of Spain and King Filip III of Portugal
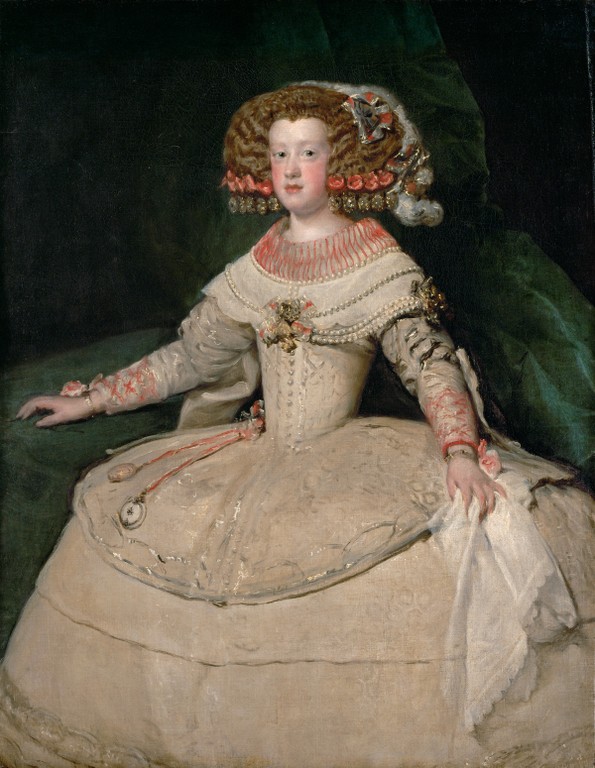

Felipe IV and Elisabeth’s only child to survive to adulthood, Maria Theresa, at age 14; Credit – Wikipedia
Felipe and Elisabeth had eight children but only their youngest child survived to adulthood. Besides having so many children die young, Elisabeth had three miscarriages. It is very probable that her husband transmitted a venereal disease he had contracted with one of his mistresses to Elisabeth. This may explain the miscarriages and the many dead infants.
- Maria Margarita of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1621)
- Margarita Maria Catalina of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1623)
- Maria Eugenia of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1625 – 1627)
- Isabella Maria of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1627)
- Balthasar Carlos of Austria, Infante of Spain, Prince of Asturias (1629 – 1646), died at age 16 from smallpox
- Francisco Fernando of Austria, Infante of Spain (born and died 1634)
- Maria Ana Antonia of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1636)
- Maria Theresa of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1638 – 1683), married King Louis XIV of France, had six children but only one son survived childhood
Elisabeth was aware of Felipe IV’s mistresses. There were rumors about her relationship with the diplomat Juan de Tassis, 2nd Count of Villamediana, her gentleman-in-waiting. Throughout her marriage, Elisabeth suffered in silence over the deaths of her children and her miscarriages. The fact that Felipe IV’s mistresses gave him children – it has been estimated that Felipe IV was the father of at least thirty illegitimate children – made Elisabeth feel even worse. Her feelings are evident in her letters to her brother King Louis XIII and sister-in-law Queen Anne of France. Weakened by her multiple pregnancies and miscarriages, Elisabeth died at the Royal Alcázar in Madrid, Spain on October 6, 1644, at the age of forty-one, after miscarrying a son. She was buried in the Pantheon of the Kings at the Royal Basilica of San Lorenzo de El Escorial.

Mariana of Austria, Felipe IV’s niece and second wife; Credit – Wikipedia
In 1646, continuing the Habsburg practice of intermarriage, Felipe IV arranged a marriage for his son and heir Balthasar Carlos, Prince of Asturias with his first cousin Mariana of Austria, the daughter of King Felipe IV’s sister Maria Anna and Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand III. However, Balthasar Carlos died three months later from smallpox, leaving his father no male heir. Three years later, on October 7, 1649, 44-year-old Felipe IV married his son’s former fiancée, his 14-year-old niece Mariana of Austria, adding to more inbreeding.
Felipe IV and Mariana had five children but only two survived childhood:
- Margarita Teresa of Austria, Infanta of Spain (1651 – 1673), married her maternal uncle and first cousin Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, had four children, only one survived infancy
- Maria Ambrosia de la Concepción of Austria, Infanta of Spain (born and died 1655), died in infancy
- Felipe of Austria, Infante of Spain, Prince of Asturias (1657 – 1661), died in childhood
- Fernando of Austria, Infante of Spain (1658 – 1659), died in infancy
- Carlos II, King of Spain (1661 – 1700) married (1) Marie Louise d’Orléans, no children (2) Maria Anna of Neuburg, no children

Felipe IV and Mariana’s son King Carlos II of Spain had a severe type of mandibular prognathism (Habsburg jaw); Credit – Wikipedia
The Spanish House of Habsburg would end with the reign of Felipe IV and Mariana’s physically and mentally disabled son Carlos II, King of Spain. While a person in the fifth generation normally has thirty-two different ancestors, Carlos II had only ten different ancestors in the fifth generation. Seven of his eight great-grandparents were descended from Juana I, Queen of Castile and León and her husband Philip of Habsburg, Duke of Burgundy. See the family tree of the ancestors of Felipe IV’s parents, Felipe III and his wife, at Wikipedia: Family Tree of Felipe III of Spain.
Carlos II’s Habsburg jaw (mandibular prognathism), a disfiguring genetic disorder in which the lower jaw outgrows the upper jaw, was so severe that he swallowed his food without thoroughly chewing. He did not learn to walk until he was eight and never was educated as befitted the heir to the throne. Carlos II died at the age of thirty-eight. Neither of his two marriages produced children, and so Carlos was succeeded by 16-year-old Philip of Anjou, the French grandson of his elder half-sister Maria Theresa of Austria and King Louis XIV of France who reigned as Felipe V, King of Spain, the first Spanish king of the House of Bourbon which is still the reigning house of Spain.

Felipe IV painted by Diego Velázquez in 1656; Credit – Wikipedia
Felipe IV, King of Spain is best remembered for his patronage of the arts, including supporting such artists as Diego Velázquez, and his rule over Spain during the Thirty Years’ War (1618 – 1648), one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history. In 1640, Felipe IV lost the Kingdom of Portugal which the King of Spain had held since 1580. The Portuguese House of Braganza came to power in Portugal after deposing the Spanish Habsburg dynasty in the Portuguese Restoration War, resulting in João, 8th Duke of Braganza becoming King João IV of Portugal. During the reign of Felipe IV, the Spanish Empire reached approximately 4.7 million square miles/12.2 million square kilometers in area. However, in other aspects, the Spanish Empire was in decline, and Felipe IV’s inability to achieve successful domestic and military reform was part of the reason.
In early September 1665, Felipe IV began to feel unwell. His stools were bloody which meant he may have had dysentery. After great suffering, Felipe IV, King of Spain, aged 60, died on September 17, 1665, at the Royal Alcázar of Madrid, located at the site of today’s Royal Palace in Madrid, Spain. He was interred in the Pantheon of Kings at the Royal Basilica of San Lorenzo de El Escorial.
Felipe IV’s second wife Mariana of Austria was appointed Regent for their three-year-old son Carlos II, King of Spain. Due to Carlos’ physical and mental issues, Mariana remained an influential figure during his reign, until her death. She survived her husband by thirty-one years, dying on May 16, 1696, at Uceda Palace in Madrid, Spain, at the age of sixty-one.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Works Cited
- En.wikipedia.org. 2022. Mariana of Austria – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mariana_of_Austria> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
- En.wikipedia.org. 2022. Philip IV of Spain – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philip_IV_of_Spain> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
- Es.wikipedia.org. 2022. Felipe IV de España – Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre. [online] Available at: <https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Felipe_IV_de_Espa%C3%B1a> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
- Flantzer, S., 2019. Elisabeth of France, Queen of Spain, Queen of Portugal. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/elisabeth-of-france-queen-of-spain/> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
- Flantzer, Susan, 2022. Felipe III, King of Spain, King of Portugal. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/felipe-iii-king-of-spain/> [Accessed 9 October 2022].
- Wheatcroft, Andrew (1995). The Habsburgs. London: Viking.